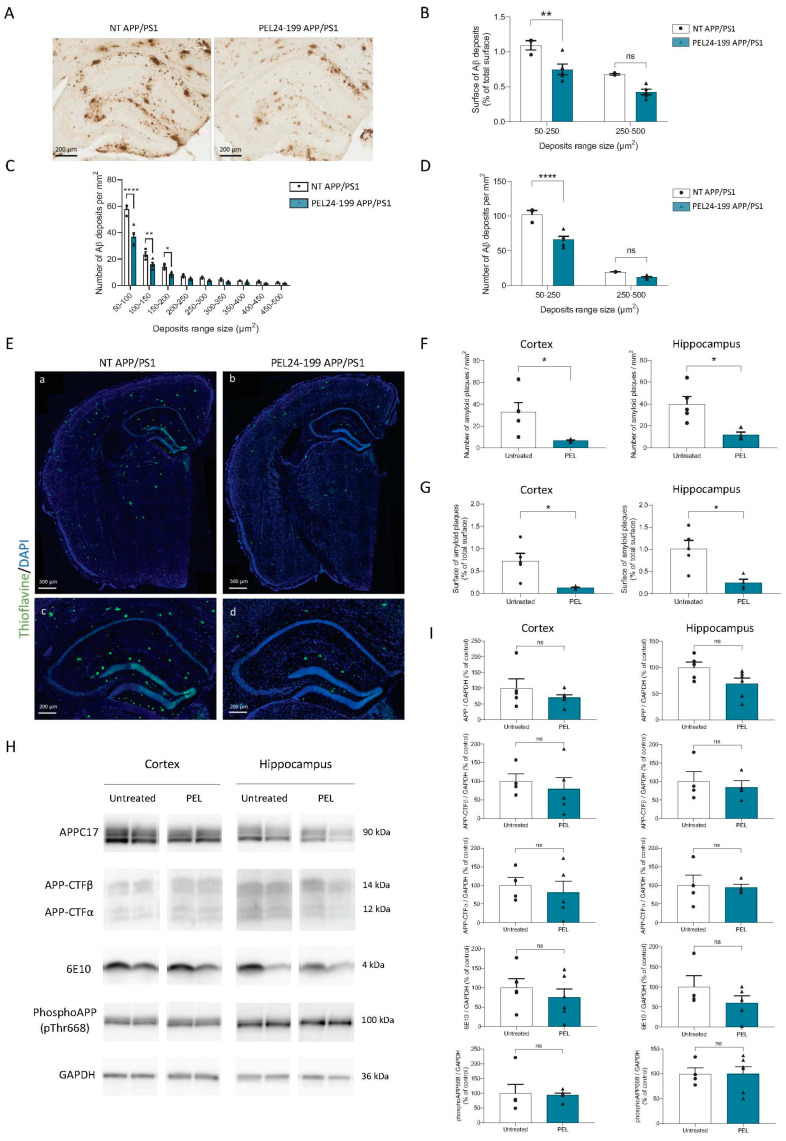
Figure 2.
PEL24-199 decreases Aβ deposits and amyloid plaque burden in APP/PS1 mice. (A) Representative images of 4G8 staining in the hippocampus of a twelve months-old APP/PS1 treated with water or PEL24-199. Scale bar = 200 µm. Aβ deposit distribution (B), size, and number (C,D) were examined in the hippocampus and the cortex of APP/PS1 mice treated or not with PEL24-199. We found that the treatment with PEL24-199 significantly reduced both in the cortex and hippocampus the surface of Aβ deposits (B) and the density of plaques of lower size (between 50–250 µm2) as compared with APP/PS1 untreated animals (50–250 µm2, p < 0.0001 using Two-Way ANOVA; n = 4–5 per group) (C–E) Representative images of Thioflavin-S (green) and DAPI (blue) staining in the hippocampus of a twelve months-old APP/PS1 treated with water or PEL24-199. Upper panels: scale bar = 500 µm; Lower panels: scale bar = 200 µm. The number (F) and surface (G) of Thioflavin-S-positive plaques per mm² were investigated in the cortex and hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice treated or not with PEL24-199. Both in the cortex and hippocampus, the surface and a number of amyloid plaques were significantly decreased. Significance at the Mann-Whitney statistical test is indicated by *: p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001, and ns as not significant. (H,I) Western blot analysis was performed in the cortex and hippocampus of water, and PEL24-199-treated APP/PS1 mice. The analysis did not reveal any change in total APP, Carboxy-terminal fragments (CTFs), the Aβ peptide, or phosphorylated APP at Thr668 protein levels (n = 5–6 per group). ns indicates no significance in the Mann-Whitney statistical test.