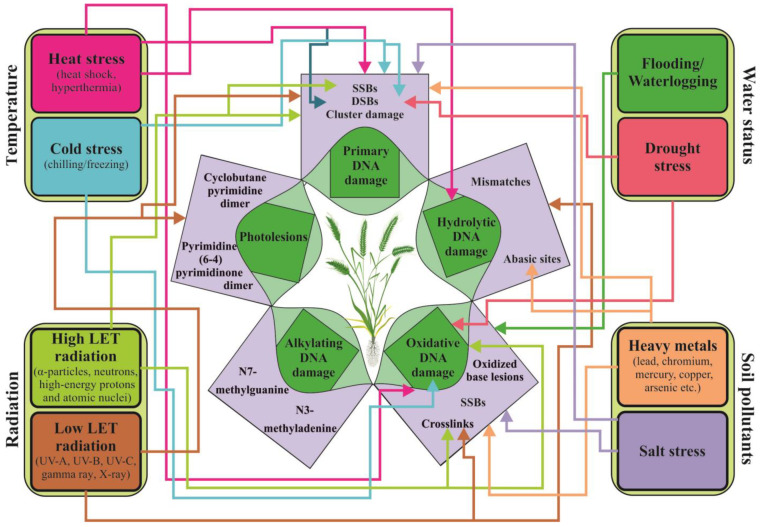
Figure 2.
Overview of the main types of DNA lesions observed in plant genomes in response to abiotic stress. Radiation as a stressor can lead to the accumulation of various types of DNA damage in plant cells, including direct DNA damage (SSBs, DSBs, and cluster damage), photolesions (6-4 photoproducts and cyclobutane-pyrimidine dimers), base damage, and interstrand crosslinks, depending on the radiation properties (high or low LET). Temperature, water, and salt stress can cause direct DNA lesions and oxidative damage due to an overproduction of ROS. Heat stress can also lead to hydrolytic lesions, similar to those caused by heavy metal stress. Primary alkylated damage is not connected to the stress factors shown in the figure as it results from the application of alkylating agents, which are not typical stress factors for plants. The relationships between specific DNA lesions and stress factors are indicated by arrows.