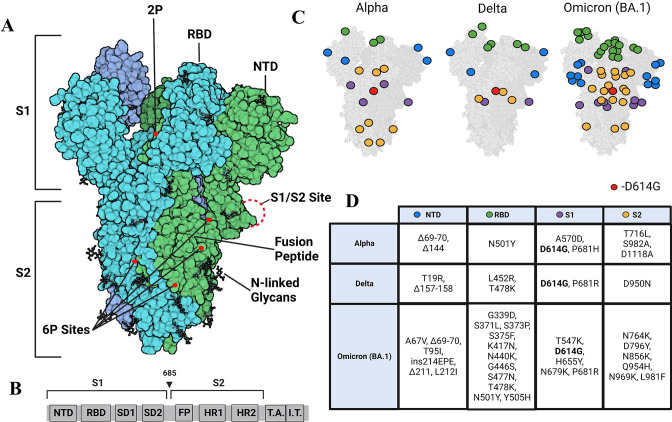
Figure 1. Strimer modifications and variant mutations.
(A) The Spike (S) protein trimer (PDB:6VSB) (protomers in dark blue, teal, and green) with receptor-binding domain (RBD), N-terminal domain (NTD), S1/S2 site, fusion peptide, 2P substitutions (985-986), additional 6P substitutions (817, 892, 899, 942), and glycans. (Image created in https://Biorender.com) (B) Sequence organization for SARS-CoV-2 S (NTD = N-terminal domain, RBD – receptor binding domain, SD1=subdomain 1, SD2=subdomain 2, FP = fusion peptide, HR1=heptad repeat 1, HR2=heptad repeat 2, T.A.=transmembrane domain, I.T.=intracellular domain). The brackets define the recombinant soluble S used in this study. Furin cleavage site (685) is indicated by arrowhead (C) Mutations in Alpha, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 S mapped onto the S structure. Mutations in the NTD, RBD, S1, and S2 domains are represented as blue, green, purple, and yellow dots, respectively, wherever a mutation can be visualized. (D) Mutations specific to Alpha, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 S variants.