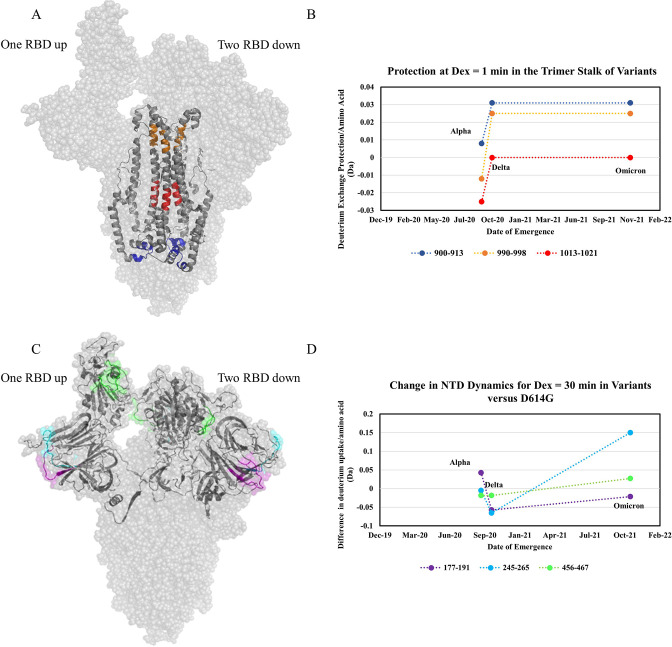
Figure 7. Increased trimer stability and altered N-terminal domain (NTD) dynamics correlate with the timeline of emergence.
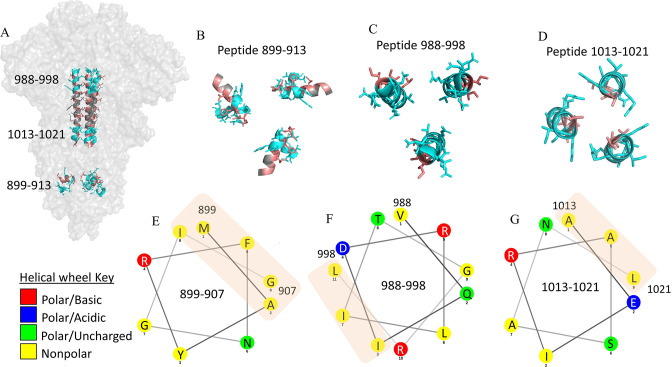
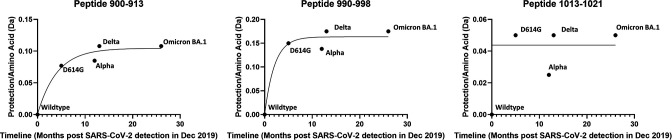
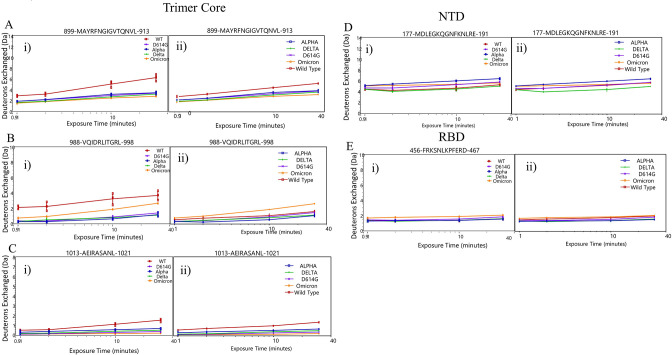
(A) Trimer stalk peptides 900–913 (blue), 990–998 (orange), and 1013–1021 (red) mapped onto a wild-type (WT) spike (S) protein structure (PDB ID: 7TGX) (helical wheel analysis of stalk peptides shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1). (B) Protection in trimer stalk peptides in S variants compared to D614G S plotted as protection per amino acid versus date of emergence at Dex = 1 min. (C) NTD and RBD peptides showing increased dynamics in the timeline of variant emergence mapped onto a 1 RBD ‘up’ WT S structure (PDB ID: 7TGX). Peptides 177–191, 245–265, and 456–467 are shown in purple, cyan, and green, respectively. (D) Changes in deuterium uptake for NTD and receptor-binding domain (RBD) peptides in variant S compared to D614G S at Dex = 30 min are plotted as a change in deuterium uptake versus date of emergence (additional plots in Figure 7—figure supplement 2). Uptake plots for representative peptides in all variants are shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 3.