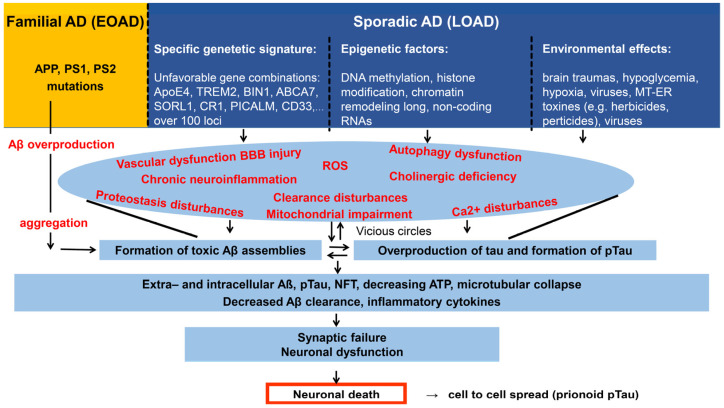
Figure 1.
The funnel model of AD. It shows the interrelated destructive processes acting in vicious circles, leading to widespread cell death. In familial AD cases (left side), mutations in APP, presenilin 1 and 2 (PS1 PS2) genes induce Aβ overproduction and formation of toxic aggregates. In the sporadic form (LOAD), aging, unfavorable gene combinations, epigenetic changes, and various environmental factors induce slow changes in the brain. Vascular and autophagy dysfunctions, BBB injury, proteostasis, and clearance disturbances lead to Aβ accumulation and subsequent formation of toxic Aβ and tau assemblies in vicious circles. Microtubular collapse results in synaptic failure, dysfunction, and death of neurons. Aβ and tau act in synergy in the pathological cascades.