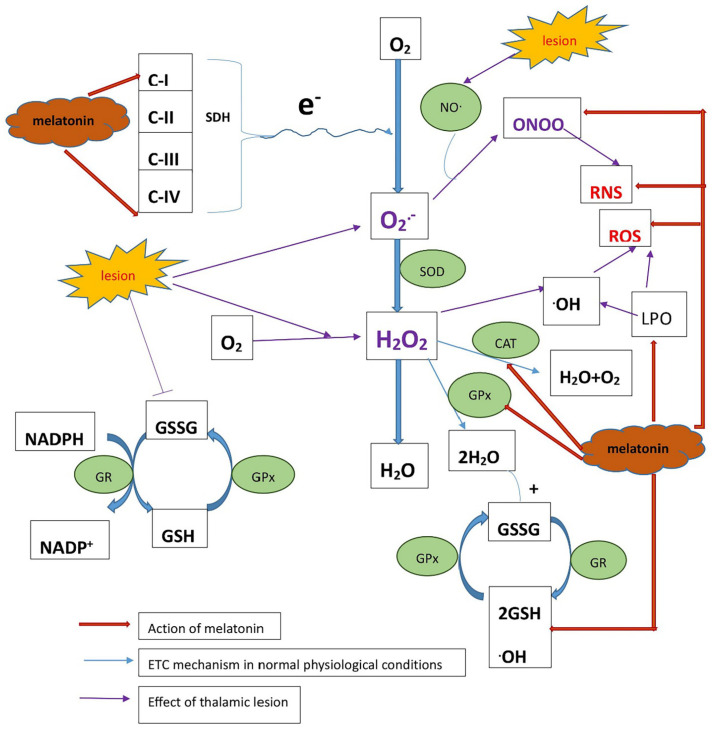
Figure 7.
The schematic representation showing an ETC chain reaction in mitochondria in normal physiological conditions, effect of lesion, and effect of exogenous melatonin treatment on ETC. In normal conditions, the electron from the transport chain progresses to form water, but due to the lesion, the oxygen free radical produces nitric oxide radicals, giving rise to RNS. Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (SOD) neutralizes the highly reactive superoxide radical O2–, known as reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under CPSP conditions due to the lesion, ROS and RNS levels increase and melatonin helps to reduce ROS and RNS.