Figure 5. Staphylococcal bicomponent leukotoxins.
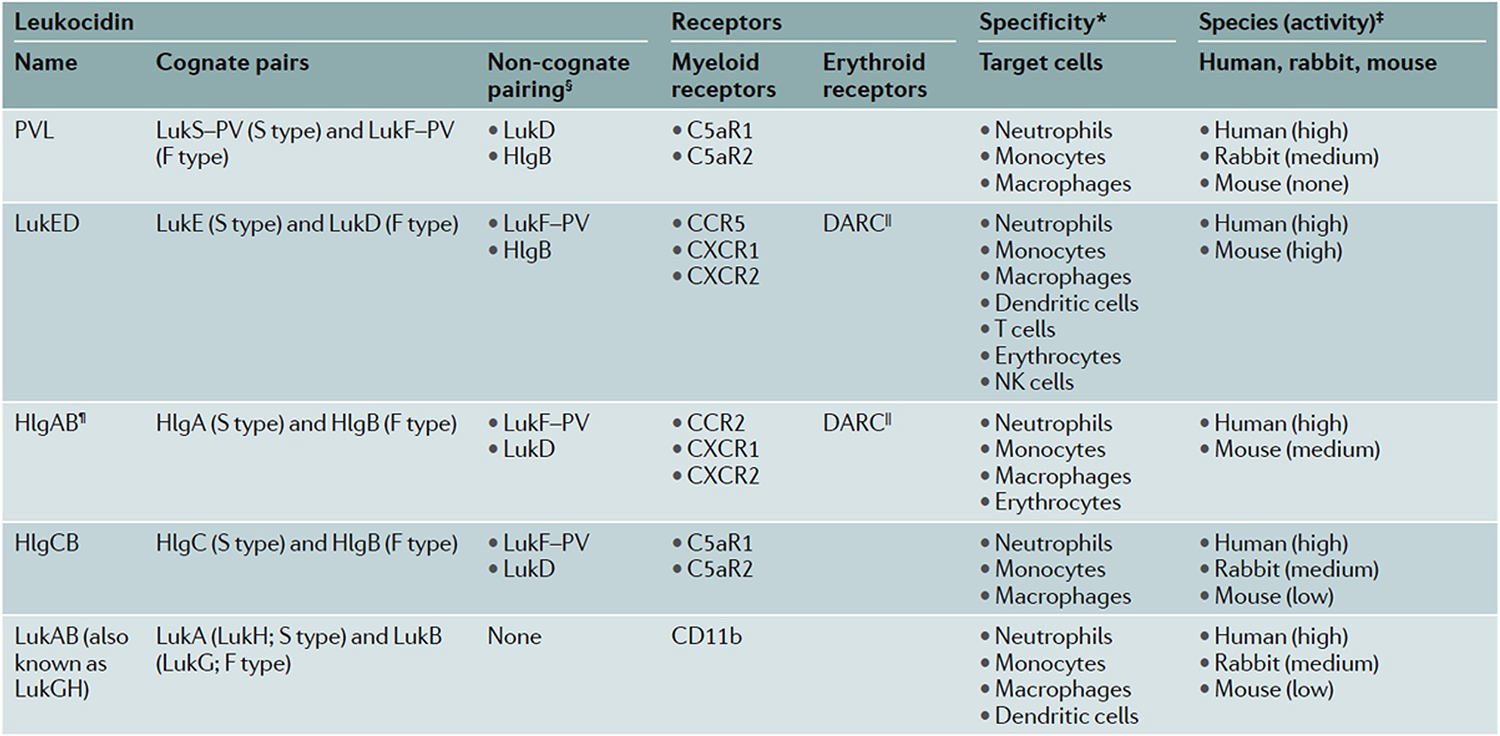
Human-adapted S.aureus produce distinct leukocidins that target myeloid and erythroid receptors with species-specific differences in susceptibility as demonstrated by experimental data (*). § designates potential pairs of the S component with an F component from another leukocidin; II indicates that DARC makes erythrocytes susceptible to the actions of LukED and HlgAB; ¶ HlgAB engages CCR2 and DARC in both human and murine cells, but only human CXCR1 and CXCR2. C5aR1, C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1; CCR2, CC-chemokine receptor 2; CXCR1, CXC chemokine receptor 1; DARC, Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines; HlgA, γ-haemolysin A; LukA, leukocidin A; NK cells, natural killer cells; PVL, Panton–Valentine leukocidin. Table originally published in 153
*Shown are the leukocytes for which there are experimental data in the literature. ‡On the basis of published susceptibility of tested primary cells. §Potential non-cognate pairing of the S component with an F component of another leukocidin. which results in functional mixed pores or inactive hybrid complexes, depending on the pair. ∥DARC renders erythrocytes susceptible to the haemolytic activity of LukED and HlgAB. ¶HlgAB targets both human and murine CCR2 and DARC, but only human CXCRl and CXCR2. CSaRl. C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1; CCR2, CC-chemokine receptor 2; CXCRl. CXC chemokine receptor 1; DARC. Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines: HlgA, y-haemolysin A: LukA. leukocidin A; NK cells, natural killer cells: PVL. Panton-Valentine leukocidin.
