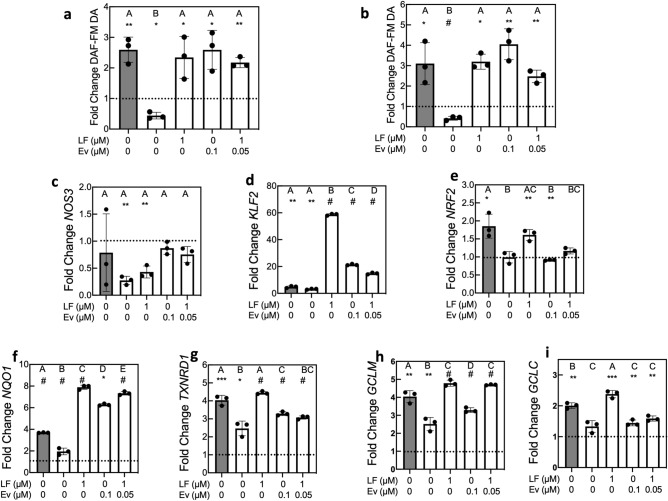
Figure 3.
Lonafarnib and Everolimus improve NO production and flow-mediated gene expression in HGPS viECs exposed to physiological shear stress. (a, b) DAF-FM diacetate (DA) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in healthy (gray), HGPS 167 CL2 (a), and HGPS 003 CL1D (b) viECs exposed to 12 dynes/cm2 for 24 h. Data presented as fold change DAF-FM DA MFI under shear stress compared with static condition from the same group. Gray bar represents healthy viECs. (c-i) Gene expression of (c) NOS3, (d) KLF2, (e) NRF2, (f) NQO1, (g) TXNRD1, (h) GCLM, and (i) GCLC in HGPS 167 CL2 viECs exposed to 12 dynes/cm2. Data were normalized to GAPDH expression and gene expression in viECs exposed to shear stress was normalized to respective viECs under static culture from the same group. Dashed line indicates normalized static control. Data presented as mean ± SD. N = 3 experiments per group. Asterisks indicate significant differences between each shear stress value and its own static control: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, #p < 0.0001. Letters indicate significant differences between treatment groups under shear stress: groups labeled with different letters are significantly different from each other (p < 0.05). Exact p-values for significant differences for comparisons between treatment groups under shear stress are provided in Table S2.