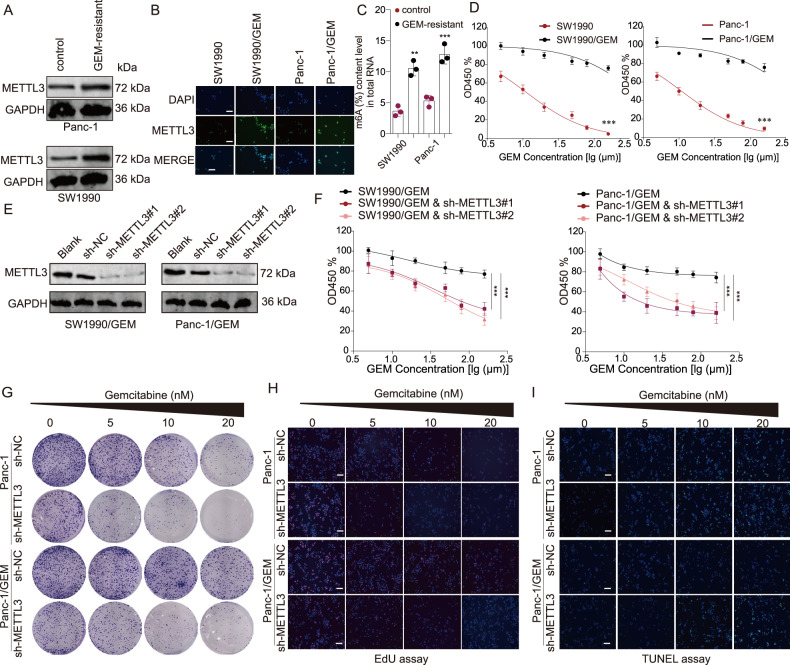
Fig. 1. METTL3 was upregulated in gemcitabine-resistant cells and the knockdown of METTL3 increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic cells.
A, B. METTL3 was upregulated in GEM-resistant Panc-1 and SW1990 cells. GEM: gemcitabine. A western blotting assay; B fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assay. C The m6A level in GEM-resistant Panc-1 and SW1990 cells was significantly higher than in corresponding parent cells. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with control group. D Both SW1990 and Panc-1 cell lines were sensitive to GEM treatment in a dose-dependent manner whereas GEM-resistant cell lines did not show significant changes across the spectrum of doses of gemcitabine. ***P < 0.001, compared with the corresponding parent cell line. E The two shRNAs against METTL3 inhibited the protein expression of METTL3 in both GEM-resistant cell lines. ***P < 0.001, compared with the GEM-resistant cell line. F The knockdown of METTL3 in GEM-resistant cells significantly increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine treatment and resulted in less cell viability (measured in optical density (OD) at 450 nm). G In both Panc-1 and GEM-resistant Panc-1 cell lines, the knockdown of METTL3 significantly increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine treatment and led to less colony formation. H In both Panc-1 and GEM-resistant Panc-1 cell lines, the knockdown of METTL3 significantly increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine treatment and led to less EDU incorporation. I In both Panc-1 and GEM-resistant Panc-1 cell lines, the knockdown of METTL3 significantly increased the sensitivity to gemcitabine treatment and led to more cell apoptosis.