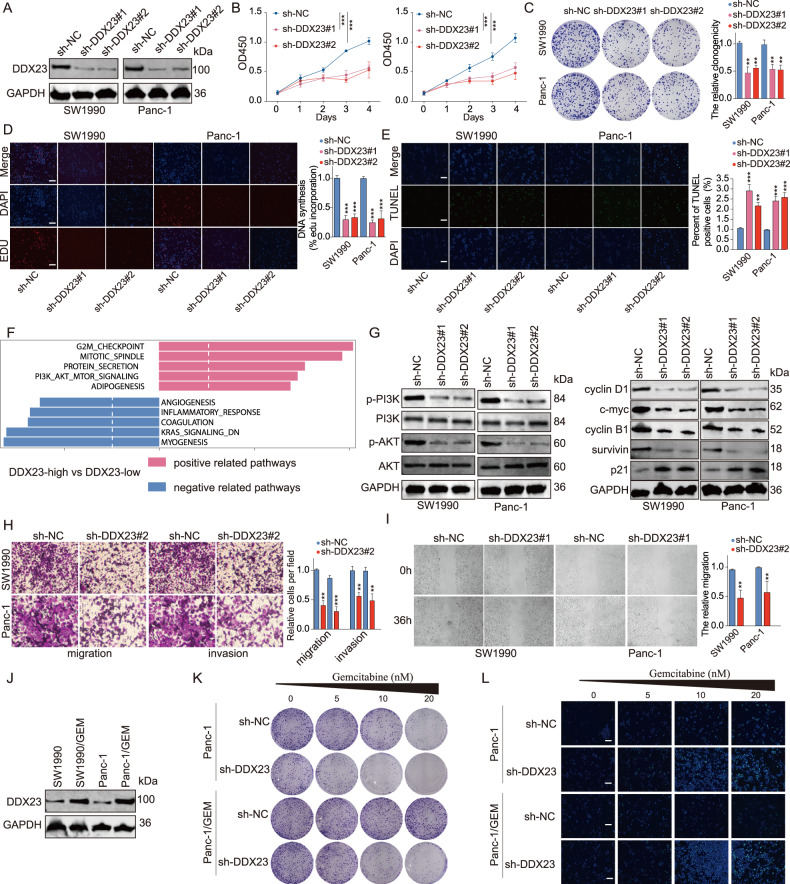
Fig. 5. The knockdown of DDX23 significantly suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion as well as resistance to gemcitabine of pancreas cancer cells via PI3K/Akt signaling.
A The two shRNAs against DDX23 significantly suppressed the expression of DDX23 protein. B In the CCK8 assay, DDX23 knockdown inhibited the optical density (OD) at 450 nm in the two cell lines. C, D In colony formation assay (C) and EDU incorporation assay (D), DDX23 silence suppressed the proliferation of the two cell lines. E In the TUNEL assay, the knockdown of DDX23 led to a significantly higher TUNEL positive cell proportion. F The signaling pathway correlation analysis result showed that DDX23 expression was positively correlated with G2M checkpoint, mitotic spindle, protein secretion, PI3K/Akt signaling, and adipogenesis, and negatively correlated with angiogenesis, inflammatory response, coagulation, KRAS signaling, and myogenesis. G The knockdown of DDX23 led to significantly inhibited p-PI3K, p-Akt, cyclin D1, c-myc, cyclin B1, survivin levels but increased p21 expression in the two cell lines. H In the Transwell assay, DDX23 knockdown led to the suppression of migration and invasion of both cell lines. I In wound healing assay, DDX23 silence resulted in the suppression of cell migration in 36 h. J In GEM-resistant cell lines, DDX23 was significantly upregulated. K DDX23 knockdown led to suppressed cell growth in the Panc-1 cell line and GEM-resistant Panc-1 cell line. L In the TUNEL assay, DDX23 knockdown resulted in significantly enhanced TUNEL positivity in the Panc-1 cell line and GEM-resistant Panc-1 cell line. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with the sh-NC group.