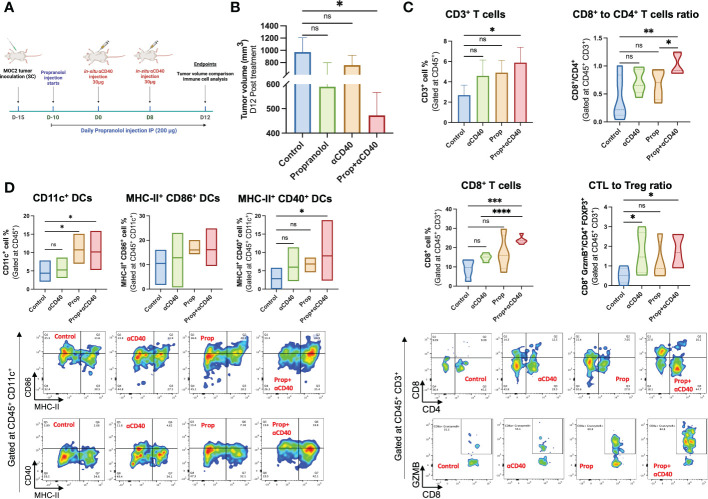
Figure 5.
Treatment design of the murine efficacy and immune-evaluation study. (A) Propranolol (10mg/kg of BW) was administered subcutaneously daily 5 days post-inoculation. Two 30 µg αCD40 intratumoral injections were administered at 8 days intervals in the tumor (~50 mm3 volume). Mean tumor volume and anti-tumor immune cells were compared on day 28 post-inoculation (Timeline created with BioRender.com). (B) The combination of Prop+αCD40 demonstrated a significant reduction in tumor volume compared to the control on day 28 post-inoculation, while monotherapies did not show any significant differences. These results suggest that the combination therapy of Prop+αCD40 is more effective in reducing tumor growth compared to either Prop or αCD40 alone. Immune cells infiltrating MOC2 tumors (n=5 mice/group) analyzed by flow cytometry showed superior immunomodulation with Prop+αCD40. (C) Frequencies of CD3+ T-cells, especially CD8+ T-cells infiltrating tumors were enhanced at the highest level by combination treatment vs untreated control and monotherapies. The ratio of cytotoxic T-cells (CD8+ GZMB+) to T regulatory cells (CD4+ Foxp3+) was increased significantly in αCD40 treated groups relative to the control. (D) CD11c+, MHC-II+ CD86+ double positive (gated at CD45+ CD11c+) & MHC-II+ CD40+ double positive (gated at CD45+ CD11c+) dendritic cell frequencies showed significant enhancements in the presence of Prop and αCD40. Statistical analysis was carried out using One-way ANOVA & Two-way ANOVA multiple comparison tests. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant. * P <0.05, ** P <0.005, *** P <0.0005, **** P <0.0001. ns, nonsignificant.