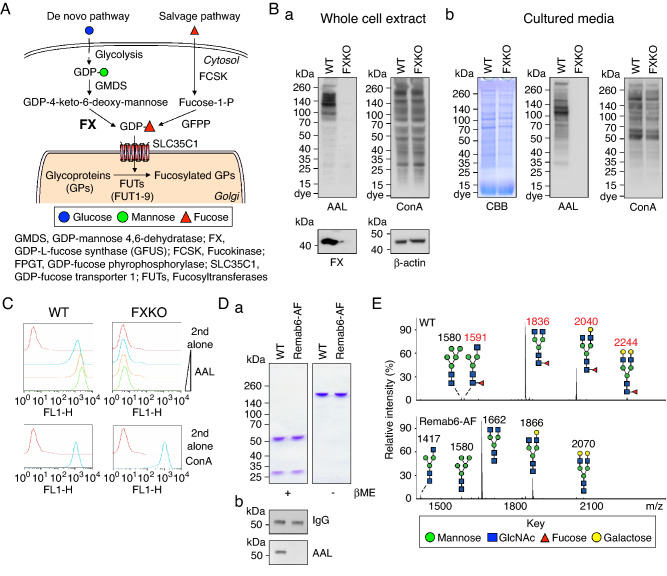
Figure 1.
Establishment of FX knockout cell line (FXKO) and generation of glycoengineered anti-Tn mAb. (A) A depiction of the L-fucose metabolic pathway in mammalian cells. (B) The FX gene knockout HEK293 free style cell line (FXKO) generated using Crispr/Cas9 system. Total cell extracts (a), or cultured media (b) from WT and FXKO cells analyzed on SDS-PAGE gel and Western and lectin blots with FX, β-actin, AAL, or ConA. SDS-PAGE gel for cultured media stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) as a loading control. (C) Fucosylation levels on cell surface analyzed by flow cytometry with AAL lectin (a 1:3 dilution ratio starting at 10 μg/mL); ConA used as a control. (D) Remab6, a chimeric anti-Tn IgG1 mAb, produced in WT and FXKO cell lines (Remab6-AF), and analyzed on SDS-PAGE gel under reducing (βME+) or non-reducing condition (βME−) stained by CBB (a), and fucosylation levels on their Remab6 analyzed by Western and lectin blots with human IgG or AAL (b). (E) N-glycome analysis of WT- or Remab6-AF produced as in (D) by MALDI-TOF–MS. The relative intensity of the most abundant peak in each spectrum set as 100% (m/z 1836, WT; m/z 1662, Remab6-AF), and selected peak masses annotated as structural features such as fucosylated (red) and non-fucosylated glycans (black). All images except Western and lectin blot (n = 3) are shown as one representative of two independent experiments (n = 2).