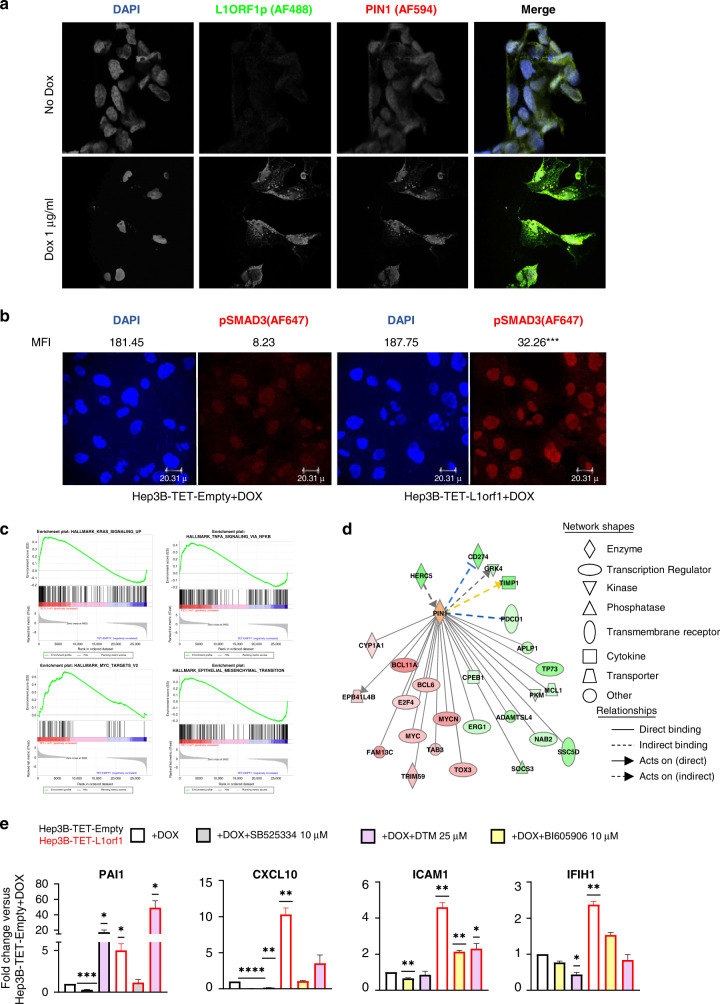
Fig. 6. Influence of L1 ORF1p overexpression on Hep3B cell lines.
a Immunocytochemical (ICC) images of Hep3B-DOX-L1 ORF1 cells costained with PIN1-AF-549 and L1 ORF1 + AF488 48 h after Dox induction. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Untreated cells were used as controls. Co-localisation analysis for Pin1 and L1 ORF1p revealed Manders coefficient M1 (proportion of the intensity from the green channel that co-localises with the red channel) = 0.958 and M2 (proportion of the intensity from the red channel that co-localises with the green channel) = 0.97; Pearson’s coefficient (co-variance of the two channels) = 0.898 for the image. b ICC images showing pSMAD3 staining of Hep3B-DOX-Empty and Hep3B-DOX-L1 ORF1 cells 48 h after Dox induction. Cells were stained with mouse-anti-pSMAD3 antibody followed by anti-mouse-AF647 secondary antibody. DAPI was used to counterstain the nuclei. MFI = mean fluorescent intensity of the indicated channel (n = 20). ****P < 0.0001 for AF647 channel, unpaired t test. c Enrichment plots obtained by GSEA upon analysing RNAseq data comparing Hep3B-DOX-L1 ORF1 versus Hep3B-DOX-Empty cells. The significance cut-off was set at FDR < 25% and p < 0.05. d Interaction map of PIN1 with differentially expressed genes in Hep3B-DOX-L1 ORF1 versus Hep3B-DOX-Empty cells. Shades of green represent downregulated and red represents upregulated genes. The orange colour of PIN1 indicates IPA predicts activation of PIN1 activity. e Graphs representing RT-qPCR results of indicated transcripts in Hep3B-DOX-Empty and Hep3B-DOX-L1 ORF1 cells upon Dox induction (1 µg/ml for 48 h) alone or in combination with the indicated inhibitor for the last 24 h. 18S was used as a normalisation control. Values represent mean ± SE of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one-sample t test with a theoretical mean of 1.