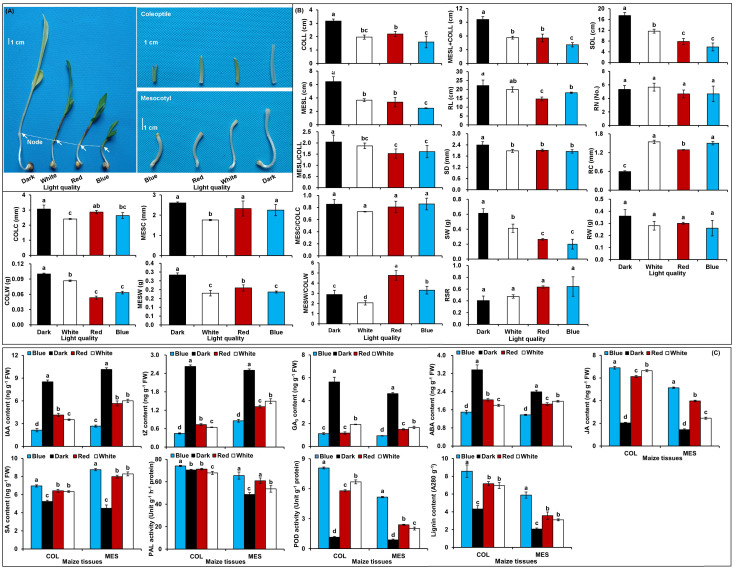
Figure 1.
Growth characteristics and physiological changes in mesocotyl (MES) and coleoptile (COL) of Zheng58 seedlings in four light stimulations. Growth of mesocotyl (MES) and coleoptile (COL) (A). Statistical analysis of multiple growth parameters including mesocotyl length (MESL), coleoptile length (COLL), total length of mesocotyl and coleoptile (MESL+COLL), ratio of mesocotyl length to coleoptile length (MESL/COLL), seedling length (SDL), root length (RL), mesocotyl coarse (MESC), coleoptile coarse (COLC), ratio of mesocotyl coarse to coleoptile coarse (MESC/COLC), seedling stem diameter (SD), root coarse (RC), mesocotyl fresh weight (MESW), coleoptile fresh weight (COLW), ratio of mesocotyl fresh weight to coleoptile fresh weight (MESW/COLW), seedling fresh weight (SW), root fresh weight (RW), root to shoot ratio (RSR), and root number (RN). Different lowercase letters in different light stimulations indicated a significant difference (p<0.05) (B). Changes in different physiological parameters, including indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) content, trans-zeatin (tZ) content, gibberellin 3 (GA3) content, abscisic acid (ABA) content, jasmonic acid (JA) content, salicylic acid (SA) content, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activity, peroxidase (POD) activity, and lignin content of MES and COL. Different lowercase letters in different light conditions indicated a significant difference (p<0.05) (C).