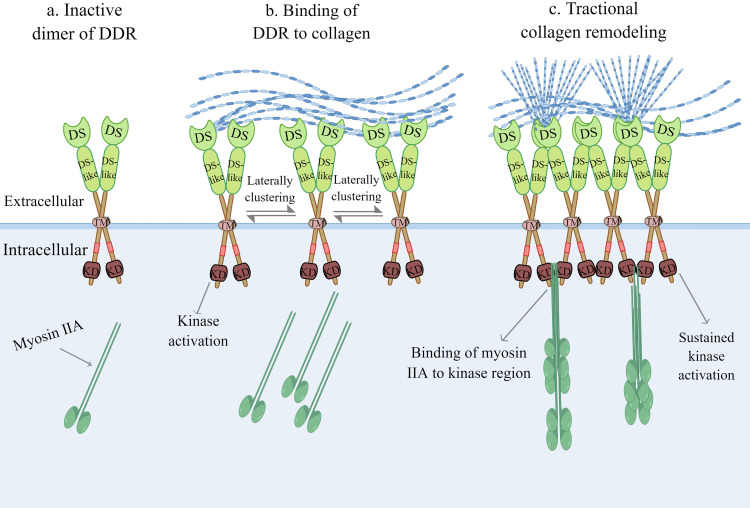
Figure 2.
Collagen-induced DDR activation. (A) Inactive dimer of DDR without binding to collagen. (B) The activation of DDR and the lateral clusters between DDR proteins are a reciprocal causation. The lateral clusters reinforce the binding of DDR to collagen, meanwhile the increasing lateral clustering of dimers are the result of collagen binding. (C) Upon kinase domain activation, DDR regulates adhesion and traction force on collagen by binding to myosin IIA, which condenses collagen fibrils into more denser alignment. DDR, discoidin domain receptor; DS, discoidin domain; KD, kinase domain; TM, transmembrane domain. (The figure is drawn by Figdraw).