Figure 4.
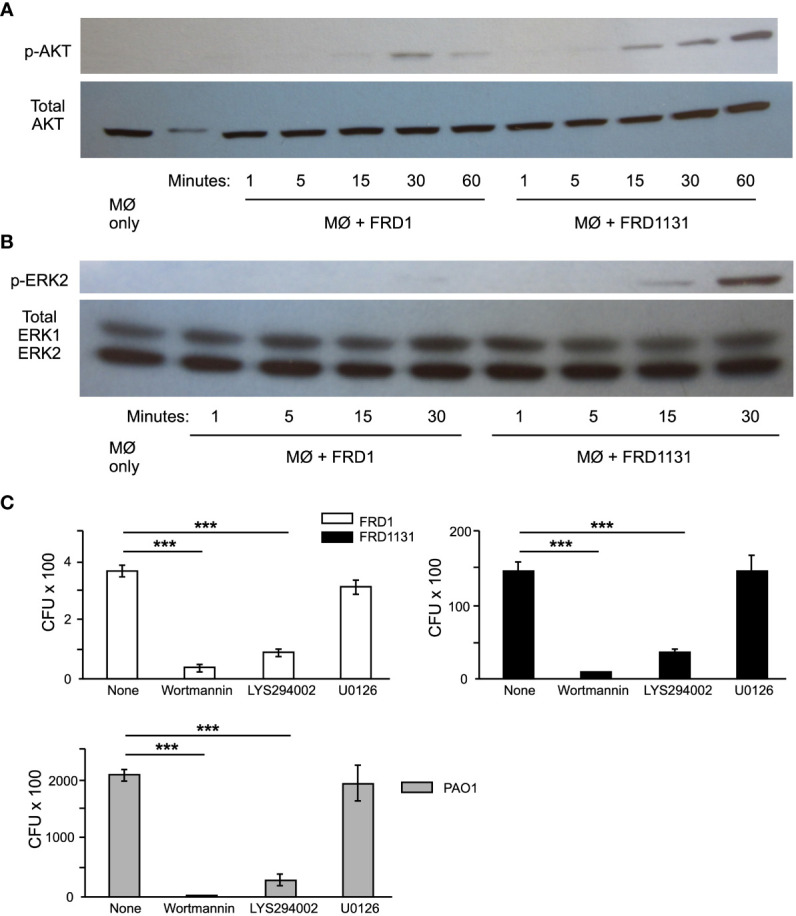
Effect of alginate production on intracellular signaling events. (A) Serum starved MH-S macrophages were infected with FRD1 or FRD1131 for 1 h. Cell lysates were collected and a Western blot was performed using anti-p-AKT and anti-pan-AKT antibodies. Infection with Alg+ FRD1 resulted in delayed AKT activation at 30 min compared to 15 min activation with FRD1131. Data shown is a representative triplicate experiment. (B) Serum starved MH-S macrophages were infected with FRD1 or FRD1131 for 30 min. Cell lysates were collected and a Western blot was performed using anti-p-ERK and anti-pan-ERK antibodies. Infection with Alg+ FRD1 resulted in decreased ERK activation at 30 min compared to Alg- FRD1131. Data shown is a representative triplicate experiment. (C) To determine the effect AKT and ERK inhibitors on phagocytosis, MH-S macrophages were infected with FRD1 or FRD1131 for 1 h in the presence of wortmannin, LY294002, or U0126. CFU indicates the number of colony-forming units recovered from macrophages. Both AKT inhibitors, wortmannin and LY294002, significantly inhibited phagocytosis of FRD1, FRD1131 and PAO1. However, the ERK inhibitor U0126 was unable to inhibit phagocytosis of any strain tested. Data are shown as mean and standard deviation of a representative triplicate experiment. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001).
