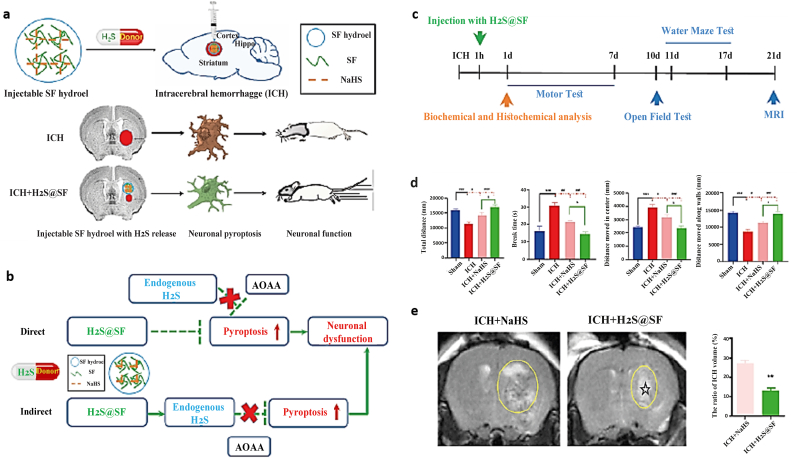
Fig. 5.
Silk fibroin (SF)-based hydrogel with sustained delivery of hydrogen sulfide decreases neuronal pyroptosis and improves functional retrieval for severe intracerebral hemorrhage. a) Schematic demonstrates the development of SF injectable hydrogel for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) treatment and shows the effective role of hydrogen sulfide sustained release in improving neuronal functionality. b) A hypothetical illustration proposes two possible ways (direct or indirect effect) for H2S@SF. In this study, significant improvement in neurological functional outcome was achieved with the H2S@SF hydrogel by the endogenous H2S synthesis pathway as an indirect effect (because adding H2S synthase inhibitor O-(Carboxymethyl) hydroxylamine hemihydrochloride (AOAA) significantly increased the expression of pyroptosis-related proteins in the striatum). c) The timeline of all experiments is shown at a glance. d) The retrieval of ICH-induced motor function, mental function, and cognitive function was improved by injecting H2S@SF hydrogel into the ICH. e) The ratio of ICH volume was evaluated after 21 days by T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), indicating a decrease in mice brains injected with H2S@SF hydrogel. The zone with irregular T2WI signals and its related zone is specified (yellow) on the ipsilateral side. Stars (☆), injected hydrogel (∗∗P < 0.01 vs. ICH group) [214]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.