Fig. 9.
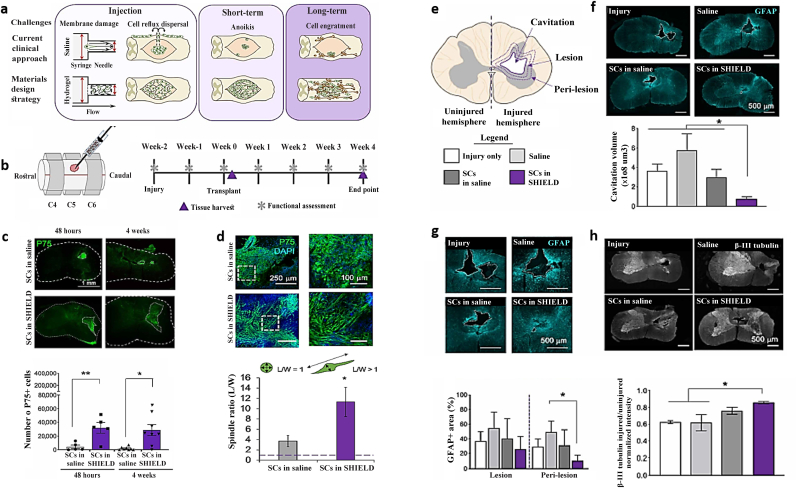
Shear-thinning Hydrogel for Injectable Encapsulation and Long-term Delivery (SHIELD) in a rat model of cervical SCI. a) Schematic illustrating three major problems that SCs have during the transplantation procedure. b) SCI model schematic. Fischer rats are subjected to a right 75-kdyne contusion injury following a C5 laminectomy. SCs are injected directly at the damage site two weeks later (subacute phase) utilizing an automated syringe needle equipment. c) Fluorescent pictures and assessment of the number of P75+ cells in spinal cord explants transplanted with SCs in SHIELD or saline (at 2 days and 4 weeks following transplantation). d) Fluorescent pictures and measurement of P75+ SCs morphology 2 days after transplantation show remarkable morphological changes between cells given in SHIELD and saline. e) Diagram of secondary injury characterization in spinal cord slices showing cystic cavitation, adjacent lesion and peri-lesion zones, and uninjured and injured hemispheres. f) Representative whole-scan fluorescence pictures and assessment of cavitation volume of spinal cord slices show cavity areas in all groups. g) GFAP staining to demonstrate the development of glial scars and to quantify the GFAP-positive region around the cystic cavity. h) Fluorescent images of β III-tubulin–stained spinal cord explants [219]. Copyright 2020 Science.