Figure 1. Argentine Ant ( Linepithema humile ) extracts induce an osm-9 dependent chemotaxis response in C. elegans .
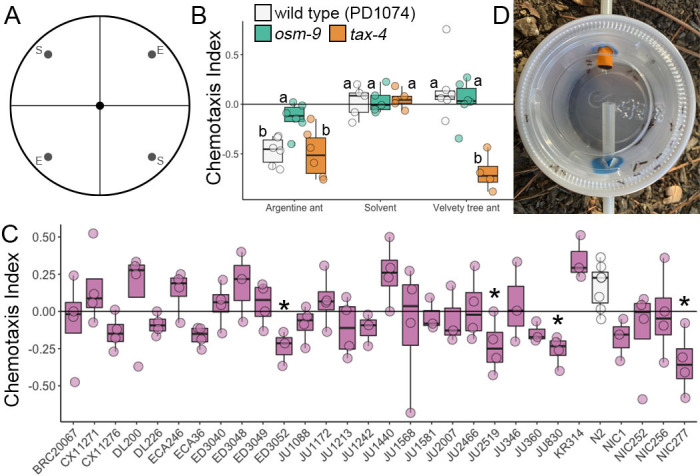
(A) Chemotaxis assays were performed on circular plates divided into quadrants, where worms placed in the center were exposed to ant extracts (E) and solvent (S). (B) The chemotaxis response of wild-type worms ( PD1074 , white), osm-9 ( ky10 ) worms (orange), and tax-4 ( p678 ) worms (blue) were tested in response to Argentine ant ( Linepithema humile) and Velvety tree ant ( Liometopum occidentale ) extracts. Wild-type PD1074 and tax-4 knockout worms, but not osm-9 knockout worms, were repelled by Argentine ant extracts. Wild-type PD1074 and osm-9 knockout worms did not respond to Velvety tree ant extracts, whereas tax-4 knockout worms were repelled. Groups not connected by the same letter are significantly different. (C) The response to Argentine ant extract was measured across a divergent strain set. Stars indicate significant differences between genetically diverse strains (purple) from wild type ( N2 , white). (D) Students constructed simple aspirators to collect ants.
