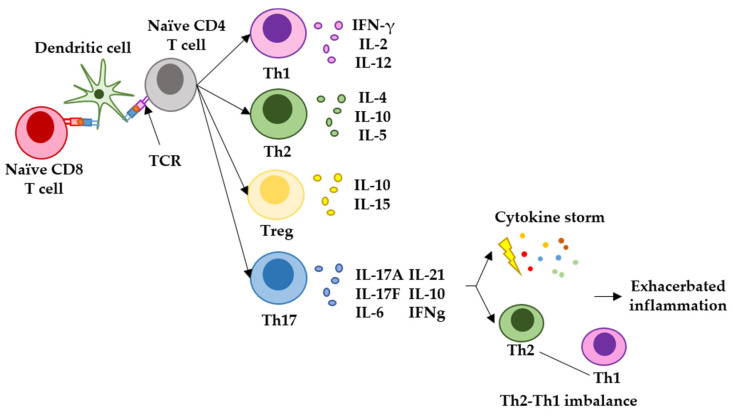
Figure 3.
Representation of the main T-helper responses after antigen presentation to CD4 T cells and the role of Th17 response in generating exacerbated inflammation. Naïve CD4 and CD8 T cells recognize antigenic peptides presented by dendritic cells through the T-cell receptor (TCR). Different T-helper pathways can be activated, but the main responses observed in infectious diseases and vaccination are represented here. The Th1 response is characterized by T cells expressing IFN-gamma and IL-2, and regulate antiviral cytotoxic responses. The Th2 response is characterized by T cells expressing mainly IL-4 and IL-10, and regulated B-cell maturation to plasma cells, leading to antibody responses and airway inflammation. T-regulatory cells express mainly IL-10 and IL-15, and inhibit autoreactive damage. Finally, the Th17 response is characterized by T cells expressing mainly IL-17, IL-6, IL-21, IL-10 and IFNgamma. Th17 responses are strong inflammatory reactions caused by an immunological stress, and can lead to cytokine storms and imbalance in Th1-Th2 responses.