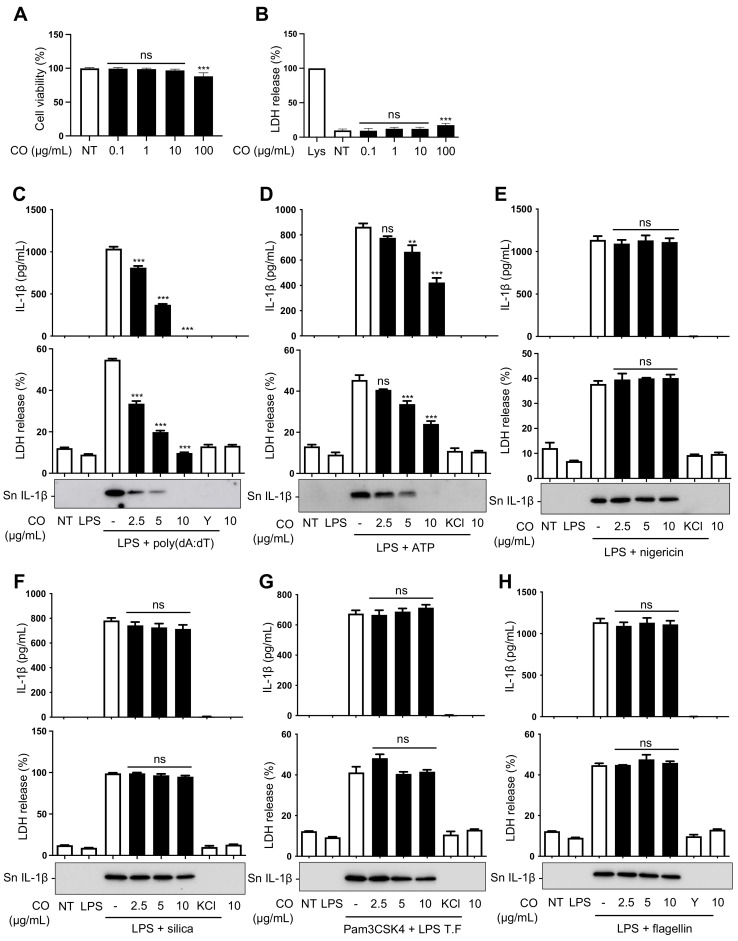
Figure 2.
CO inhibits the release of IL-1β and the cell death of LPS-primed BMDMs induced by intracellular poly(dA:dT). (A,B) Cell viability of BMDMs treated with the indicated concentrations of CO and measured by MTT and LDH assays. Data represent the means ± SDs of three independent experiments performed in triplicate; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns (non-significant) compared with the non-treated group. (C–F,H) LPS (100 ng/mL)-primed BMDMs were pre-treated with CO or 50 μM YVAD (Y) or KCl (150 mM) for 30 min and treated with (C) poly(dA:dT) transfection (1 μg/mL) for 2 h, (D) ATP (5 mM) for 1 h, (E) nigericin (10 μM) for 1 h, (F) silica (150 μg/mL) for 3 h, and (H) flagellin (1 μg/mL) transfection for 3 h. (G) Pam3CSK4 (300 ng/mL)-primed BMDMs were pre-treated with CO or KCl, as described above, then transfected with LPS (50 μg/mL) for 3 h. (C–H) Levels of IL-1β in the culture supernatants were assessed by immunoblot or ELISA assay. Occurrence of pyroptotic cell death was assessed by LDH assay. Data represent the means ± SEMs of three independent experiments performed in triplicate; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns (non-significant) compared with the LPS-primed BMDMs treated with the respective triggers.