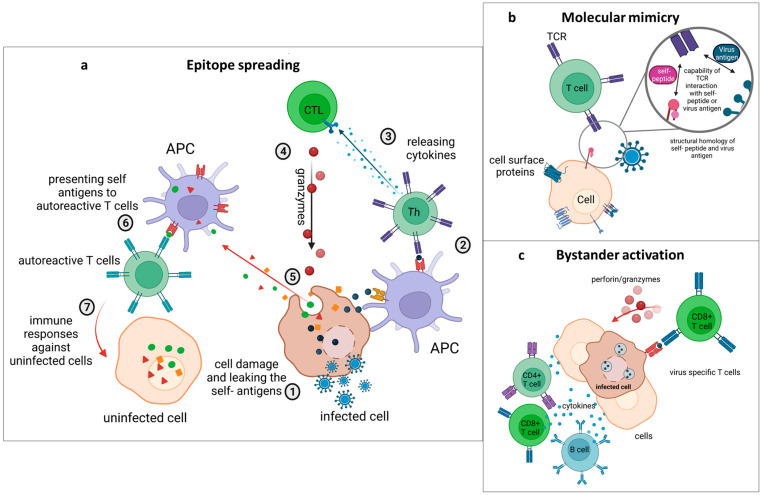
Figure 1.
Mechanisms by which virus infections cause autoimmune diseases. (a) Epitope spreading. 1. Viruses infect the host´s cells. 2. Viral antigens are presented to T-helper cells by APCs. 3. T-helper cells release cytokines, which can affect cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). 4. CTLs release granzymes, which attack infected cells. 5. Hidden self-antigens leak from damaged cells. 6. APCs present these antigens to autoreactive T cells. 7. Therefore, autoreactive T cells attack other uninfected cells carrying these self-antigens. (b) Molecular mimicry. T cell receptors (TCR) can recognize and react towards both viral antigens and self-antigens that have structural or sequential homology. (c) Bystander activation. Infected cells present viral antigens to virus-specific T cells. T cells identify infected cells and release cytotoxic granules, causing cell death of infected and nearby, uninfected cells. The inflammatory milieu leads to the activation of bystander cells within the tissue.