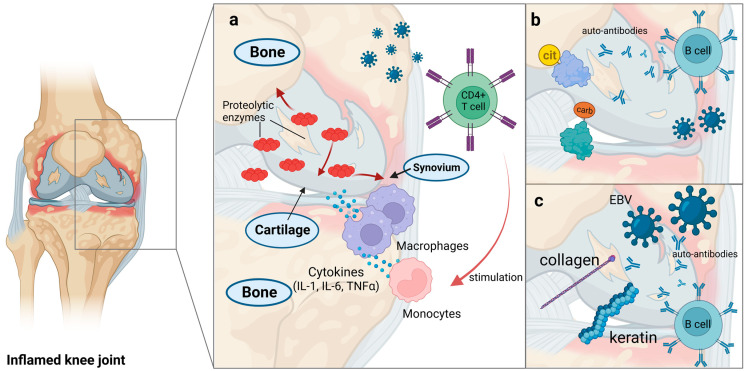
Figure 2.
Virus-induced rheumatoid arthritis. (a) Synovium, bone and cartilage damage in RA. The activated CD4+ T cells against viruses stimulate the release of cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6 and TNFα, from monocytes and macrophages. These cytokines lead to the increased release of proteolytic enzymes which cause damage of the synovium, cartilage and underlying bone. (b) Antibodies against proteins. Post-translationally changed proteins through citrullination (ACPA) and carbamylation (anti-CarP antibodies) can be identified by autoantibodies. (c) Molecular mimicry mechanism in RA. Antibodies reactive towards the primary epitope p107 of the EBV-encoded EBNA-1 antigen cross-react with keratin and denatured collagen.