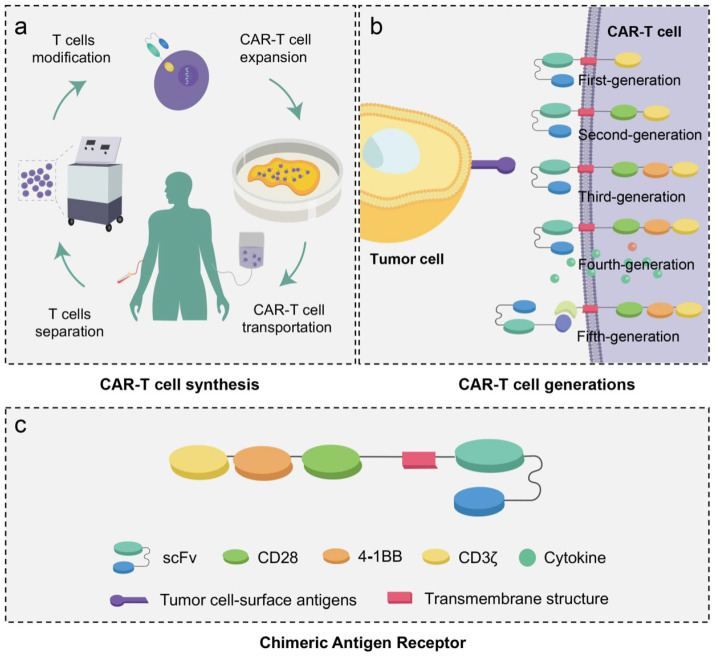
Figure 2.
Schematic of CAR-T cell synthesis and five generations of the CAR-T cell. (a) Cells are separated and collected via leukapheresis, monocyte elutriation and T-cell selection. The isolated T cells are transduced to express CAR proteins through genetic engineering. After transgene delivery, CAR-T cells are expended in vitro and transported into the patients. (b,c) CAR is composed of a single-chain variable fragment, transmembrane domain and signal domain. The signal domain of the first-generation CAR-T cell is typically composed of the CD3ζ signal chain. In second- or third-generation CAR-T cells, the structure of the signal domain contains co-stimulatory domains such as cluster of differentiation 28 and/or 4-1BB. The fourth-generation CAR-T cell is engineered to be equipped with the nuclear factor and express cytokines. The structure of CAR-T cells is still improving, and the development of a fifth-generation CAR-T cell is inevitable.