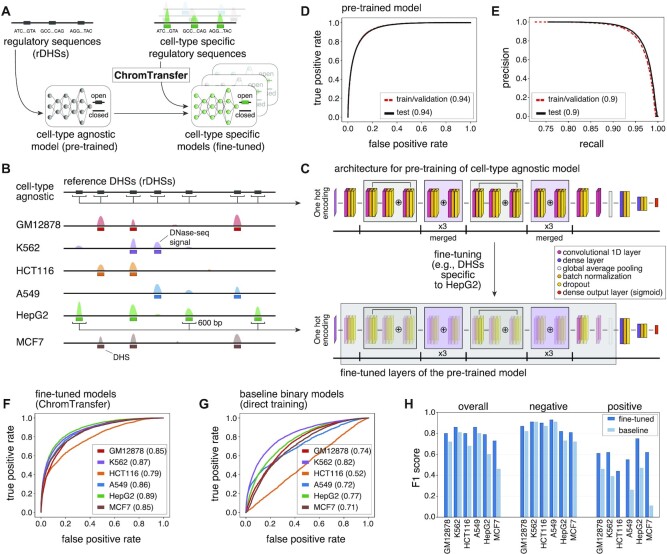
Figure 1.
Transfer learning of the sequence determinants of regulatory elements using ChromTransfer. (A) ChromTransfer is a transfer learning scheme for single-task modeling of the DNA sequence determinants of regulatory element activities. ChromTransfer uses a pre-trained, cell-type agnostic model, derived from a large compendium of open chromatin regions to fine-tune models for predicting cell-type specific activities. (B) Illustration of a genomic locus with DNase-seq signal across six cell lines along with called DHSs and the cell-type agnostic rDHS compendium. The strategy for selection of positives, 600 bp sequences centered on all rDHSs (for pre-training) or cell-type specific DHSs (for fine-tuning) are shown. (C) Model architecture (upper panel) and strategy for fine-tuning (lower panel). For network details, see Materials and Methods. (D) ROCs for training/validation and the test set of the pre-trained model for rDHS classification. AUROCs are provided in parentheses. (E) Precision recall curves (PRCs) for training/validation and the test set for the pre-trained model for rDHS classification. AUPRCs are provided in parentheses. (F, G) Test set ROCs of the six fine-tuned models (F, ChromTransfer) and the six binary class baseline models (G, direct training scheme) for classification of cell-type specific chromatin accessibility. AUROCs for each cell line model are provided in parentheses. (H) Overall and per-class (positive: open chromatin, negative: closed chromatin) test set F1 scores for the fine-tuned and binary class baseline models of the six considered cell lines. F1 scores are also given in Supplementary Table S1.