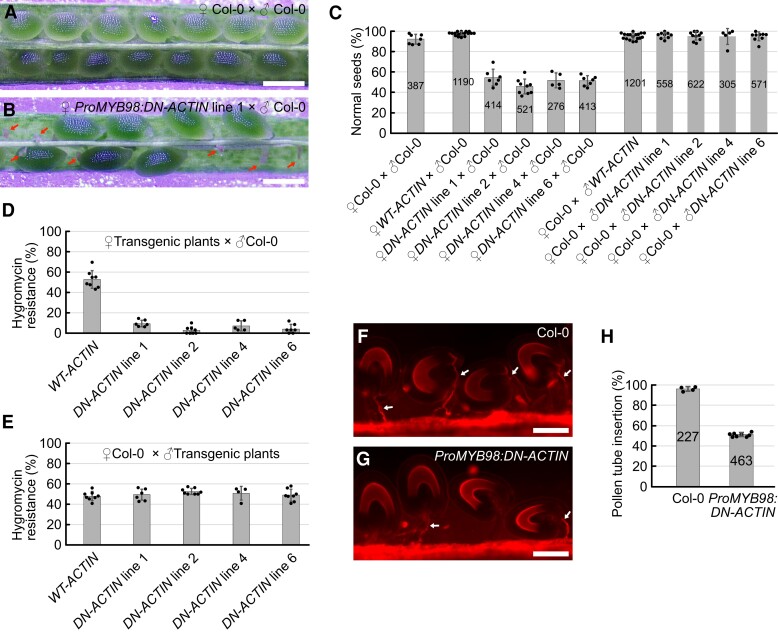
Figure 4.
F-actin is required for pollen tube attraction. A, B, Representative images of developing seeds in pistils from wild-type Col-0 plants (A), and ProMYB98:DN-ACTIN hemizygous lines (B), analyzed at 8 days after pollination with wild-type Col-0 pollen. Red arrows indicate undeveloped ovules. C, Percentages of normal seeds harvested from pistils after various combinations of cross-pollination among wild-type Col-0 plants, ProMYB98:WT-ACTIN hemizygous plants (WT-ACTIN), and ProMYB98:DN-ACTIN hemizygous plants (DN-ACTIN). D, E, Transmission of ProMYB98:WT-ACTIN and ProMYB98:DN-ACTIN transgenes via the female gametophyte (D) or male gametophyte (E). Gene transmission was analyzed by frequencies of hygromycin-resistant F1 siblings generated by cross-pollination in (B). F, G, Pollen tube growth pattern in pistils from wild-type Col-0 (F) and ProMYB98:DN-ACTIN hemizygous (line 1) (G) plants. Pistils were pollinated with wild-type Col-0 pollen and the pollen tubes were visualized by CongoRed staining at one-day-after pollination. White arrows indicate pollen tubes. H, Percentages of pollen tube-inserted ovules analyzed in (F) and (G). Data in (C-E, H) represent the mean ± Sd of the points which mean the percentage of seeds or ovules per pistil. Numbers in the bars indicate total seeds or ovules.. Scale bars: 0.5 mm in (A) and (B); 100 μm in (F) and (G).