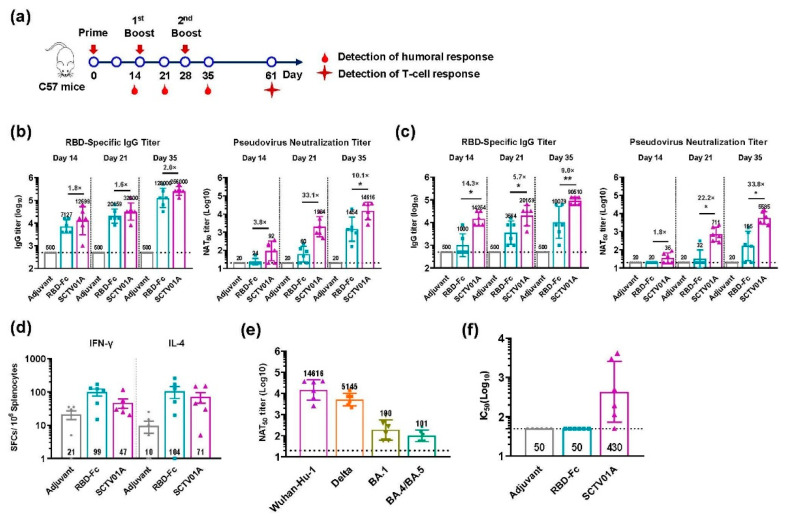
Figure 2.
SCTV01A enhances RBD-Fc-specific immune responses in C57BL/6 mice. (a) Schematic diagram of immunization and sample collection. C57BL/6 mice (n = 6/group) were intramuscularly immunized with 3 μg of SCTV01A or RBD-Fc formulated with SCT-VA02B or Alum adjuvant three times with a 14-day interval. (b) RBD specific IgG titer and NAT50 titer formulated with SCT-VA02B. (c) RBD specific IgG titer and NAT50 titer formulated with Alum. (d) The frequencies of RBD-specific IFN-γ- and IL-4-SFCs in total splenocytes were determined by ELISpot formulated with SCT-VA02B. (e) NAT50 titer against the Delta, BA.1, and BA.4/BA.5 variants of SCTV01A formulated with SCT-VA02B at Day 35. (f) OPA of SCTV01A-immunized sera as determined by opsonophagocytic assay formulated with SCT-VA02B at Day 35. The GMT of RBD-specific antibody titer and NAT50 titer against the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain were determined by ELISA and SARS-CoV-2 PsV neutralization assay. The dashed black lines indicate the limit of detection (LOD). The LOD of the RBD-specific antibody ELISA is 500, and the LOD of the SARS-CoV-2 PsV neutralization assay is 20. For detection of the T-cell response, mice were euthanized at 61 days post first immunization, and their spleens were dissected for ELISpot. For (b,c), levels of RBD-specific IgG titers and NAT50 titers were compared across SCTV01A and RBD-Fc by unpaired two-tailed Welch’s tests. * p ≤ 0.05 and ** p ≤ 0.01 represent statistical significance. The unlabeled comparisons were not significant, with p ≥ 0.05.