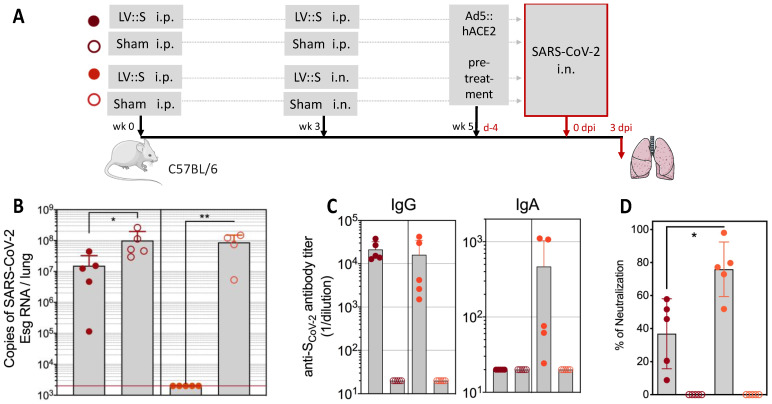
Figure 3.
An intranasal boost with LV::S fully protects against SARS-CoV-2 replication. (A) Timeline of prime (i.p.) and boost (i.p. or i.n.) with LV::S in C57BL/6 mice, followed by pretreatment with an Ad5::hACE2 vector encoding the human ACE2 receptor four days before an i.n. challenge with SARS-CoV-2. The control LV vector encodes an irrelevant antigen (sham). (B) Pulmonary viral content determined at three days post infection (dpi) by qRT-PCR specific for a subgenomic RNA (Esg) expressed only by replicating SARS-CoV-2. The red line indicates the limit of detection. (C) Titers of IgG and IgA antibodies specific for SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen, determined by ELISA, in lung homogenates. (D) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody neutralizing activity detected in lung homogenates using spike-bearing pseudoviral particles. Statistical significance of the differences was determined by the Mann-Whitney U test (* p < 0.02, ** p < 0.01). Adapted from [34] ).