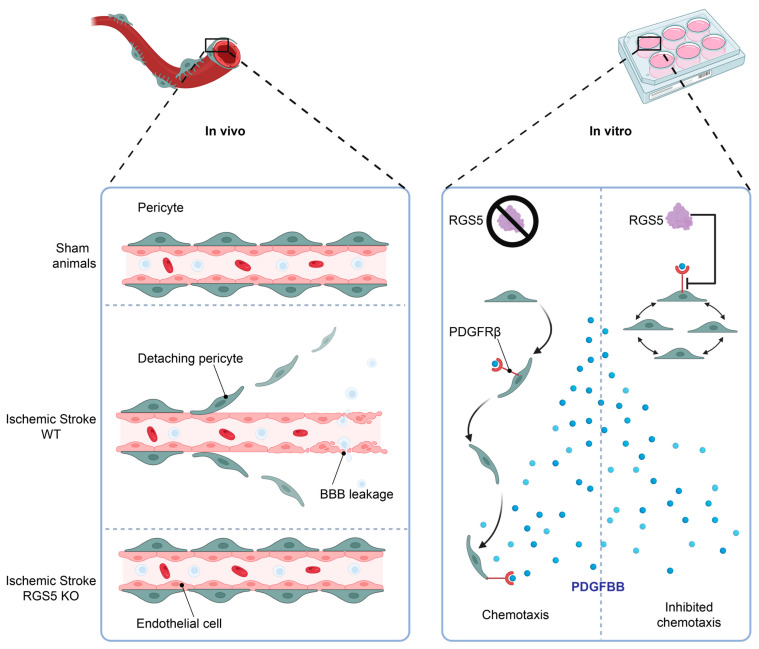
Figure 4.
RGS5 regulates pericyte migration. Following stroke onset, the ischemic microenvironment induces RGS5 stabilization in WT pericytes, correlating to pericyte detachment from the blood vessels and migration into the brain parenchyma, leading to BBB leakage. However, in RGS5 KO mice, pericytes remain attached to the vascular wall, reducing BBB leakage and vascular damage (left panel). In addition, RGS5 expression in human brain pericytes inhibits PDGFBB chemotaxis (right panel), which could be a possible contributing factor to the pericyte detachment observed in vivo, as PDGFBB is a key regulator of pericyte recruitment and retention to the vascular wall. Created with BioRender.com, 18 February 2023.