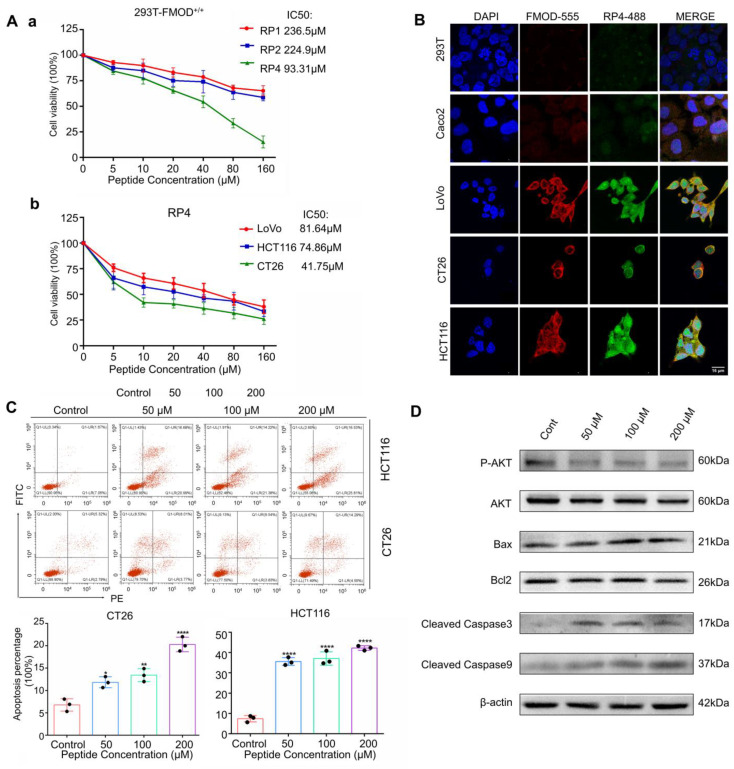
Figure 3.
RP4 binds to FMOD and inhibits the growth of CRC cells. (A) (a), Cell viability of 293T FMOD+/+ treated with indicated concentrations of RP1, RP2, and RP4 for 48 h. (b), Cell viability of LoVo, HCT116, and CT26 treated with indicated concentrations of RP4 for 48 h. (B), Cellular localization of RP4 and FMOD by confocal immunofluorescence. (C), HCT116 and CT26 cells were stimulated with indicated concentrations of RP4 for 48 h and then co-stained with PI and FITC conjugated Annexin V. The apoptosis of cells was detected by flow cytometry. (D), Western blotting results of CRC cells treated with RP4. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA (n = 3; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001). Representative images from three independent experiments are shown.