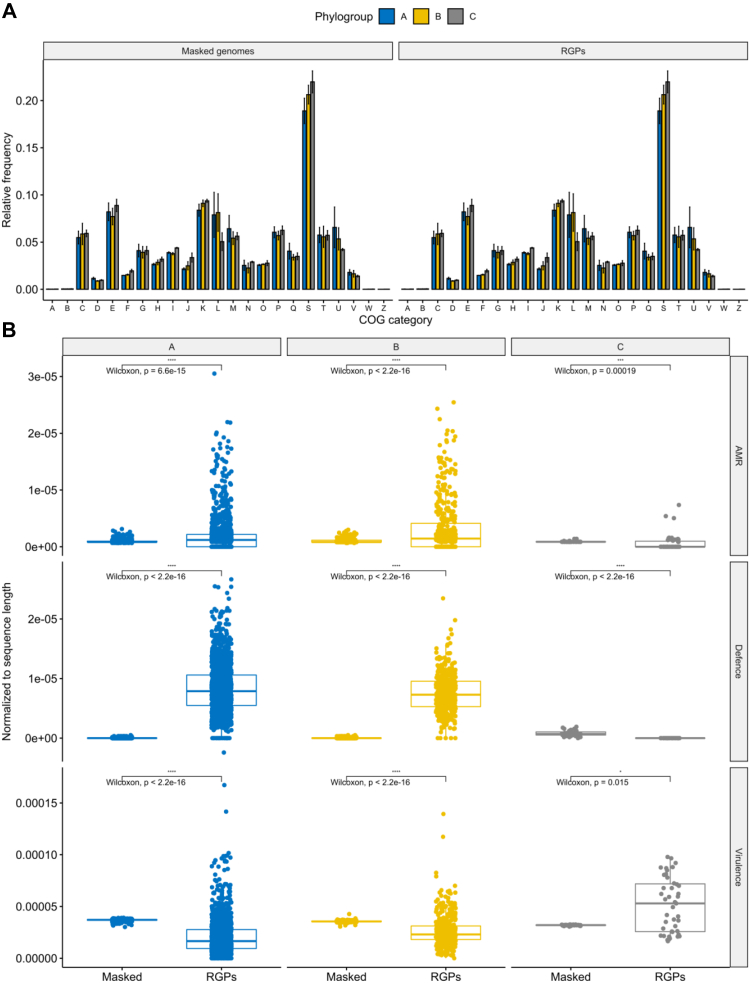
Fig. 5.
Distribution of functional categories across RGPs and masked genomes from the different phylogroups. Bar and boxplots in blue represent phylogroup A, yellow B, and grey C. (A) Relative frequencies of cluster of orthologous groups categories. The relative frequencies were calculated by dividing the absolute counts for each category by the total number of clustered proteins found in each of the six groups. Error bars indicate the degree of variation across each COG category from each phylogroup across RGPs and masked genomes. The functional categories are indicated by capital letters, including: A, RNA processing and modification; B, chromatin structure and dynamics; C, energy production and conversion; D, cell cycle control and mitosis; E, amino acid metabolism and transport; F, nucleotide metabolism and transport; G, carbohydrate metabolism and transport; H, coenzyme metabolism; I, lipid metabolism; J, translation; K, transcription; L, replication, recombination and repair; M, cell wall/membrane/envelop biogenesis; N, cell motility; O, post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperone functions; P, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, secondary structure; R, general functional prediction only; S, function unknown; T, signal transduction; U, intracellular trafficking and secretion; V, defence mechanisms; W, extracellular structures; Z, cytoskeleton. (B) Boxplots of the variation in the number of AMR genes, defence systems, and virulence genes found in RGPs and masked genomes across the three phylogroups. Absolute counts of genes and systems were normalized to RGP and masked genome sequence lengths in each strain. Values above 0.05 were considered as non-significant (ns). Stars indicate significance level: ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001.