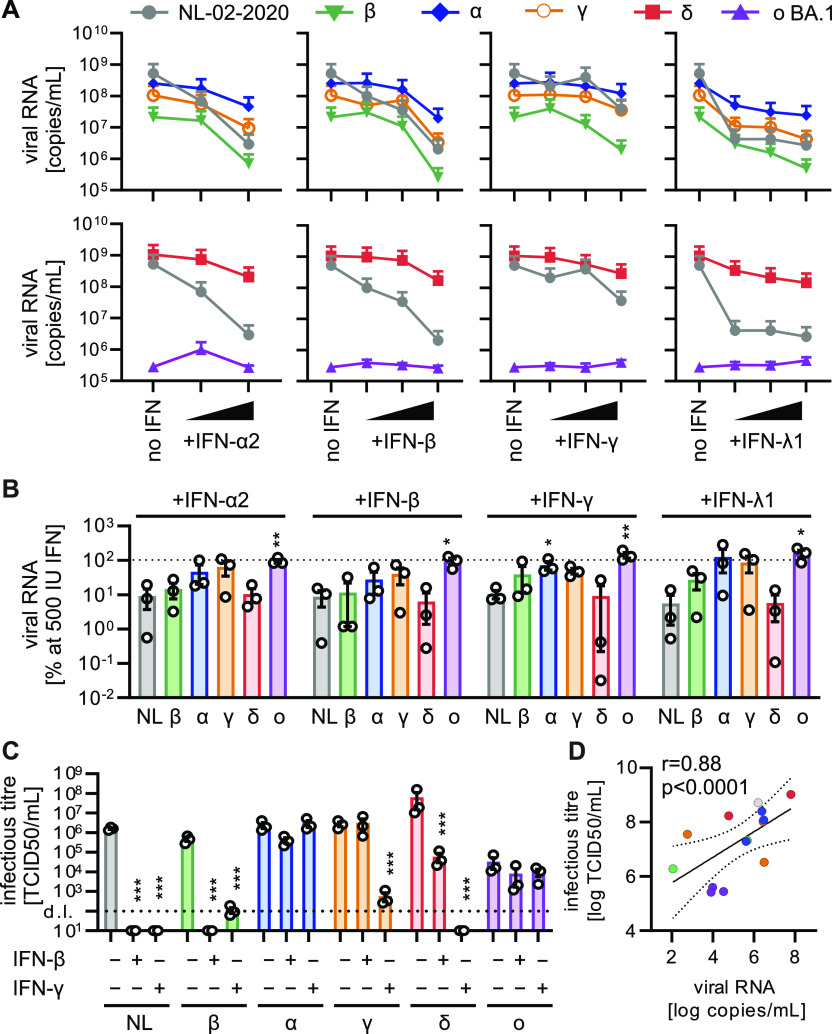
Figure 1. IFN sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Calu-3 cells.
(A) Viral RNA in the supernatant of Calu-3 cells infected with indicated SARS-CoV-2 variants was quantified by qRT–PCR at 48 h postinfection (MOI 0.05). Cells were treated preinfection with increasing concentrations of indicated IFNs (α2 at 5 and 500 IU/ml, β, and γ at 5, 50, and 500 IU/ml or λ1 at 1, 10, and 100 ng/ml). Dots represent the mean of n = 3 + SEM. (B) Percentage of viral RNA in the supernatant compared with the no IFN control (set to 100%) at 500 IU/ml IFN (100 ng/ml for IFN-λ1) as indicated. Bars represent the mean of n = 3 ± SEM. (C) Infectious SARS-CoV-2 particles determined by the TCID50 assay in the supernatant of Calu-3 cells infected with indicated SARS-CoV-2 variants (MOI 0.05, 48 h postinfection). Cells were left untreated or were pretreated with 500 IU/ml IFN-β or IFN-γ. Bars represent the mean of n = 3 ± SEM. d.l., detection limit. (B, C, D) Correlation of infectious titer of viral particles ((C), TCID50) with viral RNA in the supernatant ((B), qRT–PCR), r, Pearson’s correlation. Statistical significance was calculated using t tests. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.