Table 2.
CS derivatives applied as antivirals or antiviral carriers, with properties and preparations.
| CS Derivatives | Formula | Physical Properties | Biological Properties | Preparation Method | Advantages/Limitations/Potential Uses | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic Derivatives | ||||||
| Quarternized derivatives |
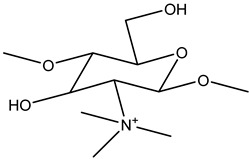
|
-cationic derivatives -water-soluble at neutral pH -N,N, N-trimethyl CS chloride (TMC) ↑ aqueous solubility than CS |
-biocompatibility -biodegradability -mucoadhesion |
-direct quaternary ammonium substitution -epoxy derivative open loop -N-alkylation |
-antifungal, antibacterial, antituberculosis -enzyme inhibition -permeation enhancers -gene transfection and delivery -good moisture retention and absorption -mucoadhesivity ↓ with ↑ degree of quaternization -↑ degree of quaternization ↓ intrinsic viscosity -pH 7.4 CS and salts failed to increase the permeability -absorption enhancer for intestinal lumen with pH close to its pKa -TMC collects and delivers more negatively charged DNA/genes than plain CS -quaternized CS ↑ hydroxyl radical scavenging activity in comparison to other CS -pH-sensitive targeting |
[184] |
| Sulfated derivatives |
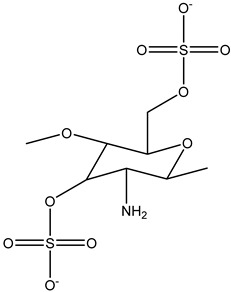
|
-water-soluble sulfoethylated CS with improved swelling property -during sulfation, some amino groups of CS are converted to anionic centers, which leads to better polyelectrolyte properties -N-alkyl-O-sulfated CS has amphiphilicity since it carries long-chain alkyl groups with a hydrophobic nature and sulfated groups with a hydrophilic nature |
-biocompatibility -biodegradability |
-sulfation of 2-chloroethane sulfonic acid sodium salt in alkaline media -sulfur-containing derivatives were obtained by reacting CS with CS2, formaldehyde, and primary amine |
-antisclerotic, antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-HIV, antiviral, and enzyme inhibition -blood anticoagulant -hemagglutination inhibition activity -amphiphilic polymer enables the formation of micelles with physical entrapment of water-insoluble drugs such as taxol -structural similarity of CS salt with heparin -high sorption capacities -a great advantage for metal ion recovery |
[25] |
| CS derivatives with sugar part |
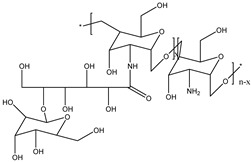
|
-water-soluble -investigated mainly for rheological studies |
-biodegradability -biocompatibility -nontoxic |
-reductive N-alkylation (using NaCNBH3 and unmodified sugar, a sugar-aldehyde derivative, or N-alkylation of CS performed in aqueous methanol with various aldehydes, monosaccharides, and disaccharides) |
-antibacterial and antimicrobial activity -this type of modification has usually been used to introduce cell-specific sugars into CS -synthesis of sugar-bound CS, such as those with D- and L-fucose, and their specific interactions with lectin and cells -lactose-modified CS for a potential application in the repair of the articular cartilage -galactosylated CS prepared from lactobionic acid and CS with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)- carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) showed promise as a synthetic extracellular matrix for hepatocyte attachment -graft copolymers of galactosylated CS with poly(ethylene glycol) or poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) were useful as hepatocyte-targeting DNA carriers |
[181,185,186] |
| CS glutaraldehyde crosslinked polymer |
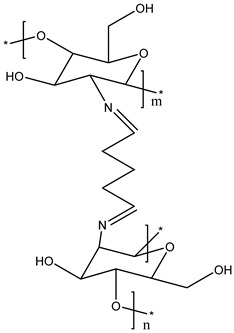
|
-improved permeability, mechanical properties, wetting, and chemical resistance -gelation temperature: 32–33 °C -viscosity of the hydrogel increased quickly after gelation |
-not cytotoxic to human corneal epithelial cells at a low concentration -biocompatibility -biodegradability |
-CS dissolved in acetic acid with glutaraldehyde performed in a short time | -N-trimethylated CS crosslinked with glutaraldehyde has been used to fabricate hollow microspheres for drug loading |
[187] |
| CS cyclodextrin derivatives |
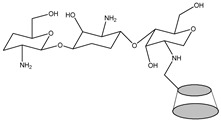
|
-can enhance the solubility of sulfadiazine, sulfamonomethoxine, and sulfamethoxazole | -antimicrobial activity -antifungal activity -bioavailability -nontoxic -biodegradability |
-physical mixing, kneading, co-precipitation, and solvent evaporation | -increases dissolution -improves stability |
[188,189,190] |
| CS oligomers |
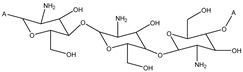
|
-soluble over a wide pH range, from acidic to basic -water-soluble |
-antioxidant activity -anti-inflammatory activity -antiviral activity -nontoxic -antifungal activity -biodegradability -biocompatibility -immunological and antibacterial activities |
-prepared from the degradation of CS -oxidative degradation method involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and combined degradation using hydrogen peroxide and microwave radiation |
-inhibit the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and iNOS, which are associated with an inflammatory response -depress oxidative stress -decrease induced cell apoptosis -alleviate or delay Alzheimer´s disease process |
[191,192] |
↑ means increase, ↓ means decrease.
