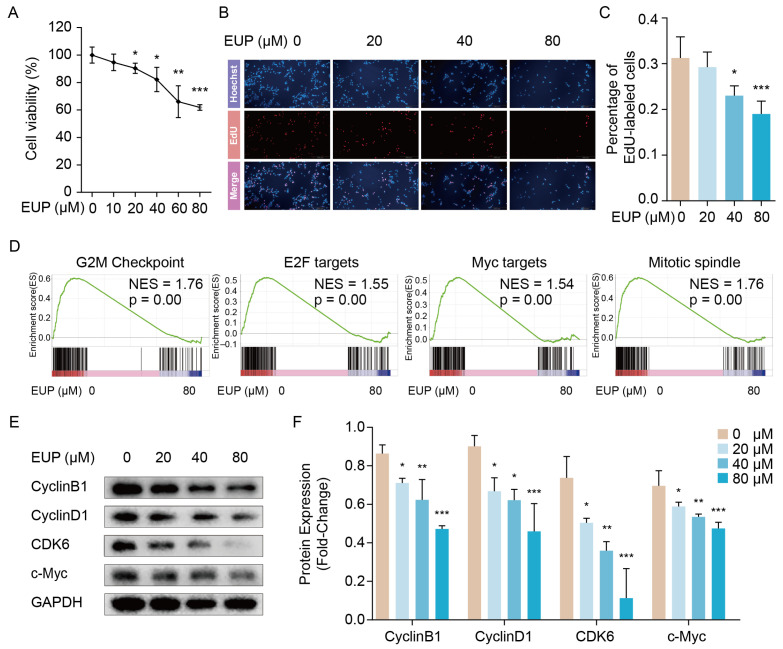
Figure 2.
Eupatilin inhibits the proliferation of LX-2 cells. (A) Cell viability of LX-2 cells treated with different eupatilin concentrations. (B) The effect of eupatilin on DNA replication of LX-2 cells investigated by EdU staining. (C) The percentage of EdU-labelled cells is plotted (mean ± SD, n = 4). (D) GSEA enrichment plots showed four proliferation-related gene sets were down-regulated in eupatilin exposed LX-2 cells. (E) The protein levels of CyclinB1, CyclinD1, CDK6, and c-Myc detected 48 h after eupatilin treatment using Western blotting. (F) Relative protein signal intensity was quantified as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD, n = 3). p values are calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 vs. 0 μM EUP group. EUP: Eupatilin; GSEA: Gene set enrichment analysis; CDK6: Cyclin dependent kinase 6; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.