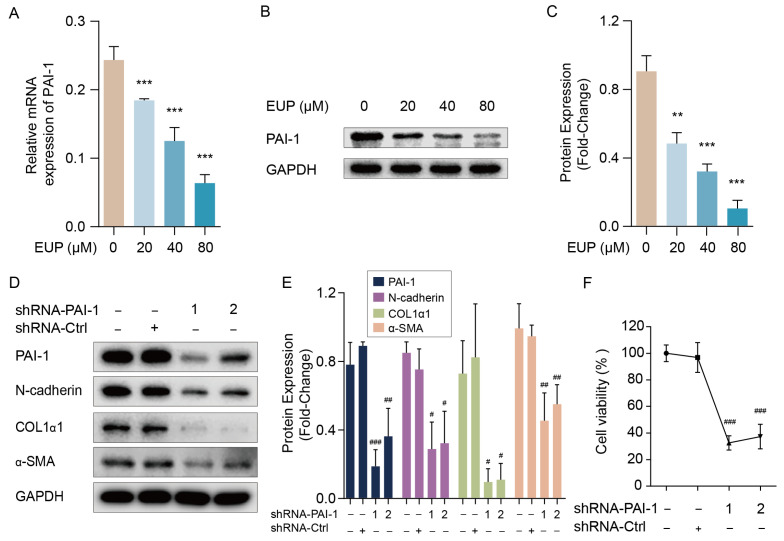
Figure 4.
PAI-1 regulates the activation of LX-2 cells involving EMT pathway. (A) Relative mRNA expression of PAI-1 in LX-2 cells when treated with eupatilin (mean ± SD, n = 3). (B) Western blot analysis of PAI-1 in LX-2 cells. (C) Relative protein signal intensity of Figure 4B was quantified as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD, n = 3). (D) Protein levels of PAI-1, N-cadherin, COL1α1 and α-SMA detected by Western blotting. LX-2 cells were transfected with control (shRNA-Ctrl) or shRNA targeting PAI-1 (shRNA-PAI-1 1 and shRNA-PAI-1 2) for 48 h. (E) Relative protein signal intensity of Figure 4D was quantified as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD, n = 3). (F) Cell viability of LX-2 cells transfected with shRNA-Ctrl or shRNA-PAI-1 detected by CCK8 assay (mean ± SD, n = 4). p values are calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s test. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 vs. 0 μM EUP group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 vs. shRNA-Ctrl group. EUP: Eupatilin; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; COL1α1: Collagen type I alpha 1; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.