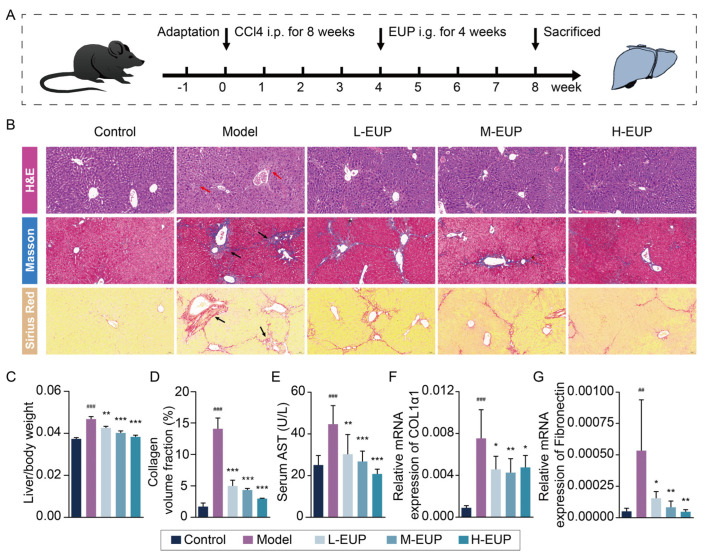
Figure 6.
Eupatilin alleviates hepatic fibrosis in CCl4-induced mouse models. (A) The scheme of animal experiments in present study. The grouping was as follows: Control; Model (CCl4, without EUP treatment); L-EUP (CCl4, 10 mg/kg EUP); M-EUP (CCl4, 20 mg/kg EUP); H-EUP (CCl4, 40 mg/kg EUP). (B) Representative images of livers stained with H&E, Masson, and Sirius red (Red arrows represent mononuclear cell infiltration, black arrows represent collagen deposition. Scale bars = 50 μm). (C) The ratios of liver weight to body weight in different groups (mean ± SD, n = 6). (D) Analysis of collagen volume fraction of Masson staining. (E) Serum levels of AST in CCl4-induced mice (mean ± SD, n = 6). (F,G) Relative mRNA expression of COL1α1 and Fibronectin in liver tissues (mean ± SD, n = 6). ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001 vs. control group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 vs. model group. p values are calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s test. CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; i.p.: Intraperitoneal; i.g.: Intragastrical; EUP: Eupatilin; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; L-EUP: Low-dose eupatilin; M-EUP: Middle-dose eupatilin; H-EUP: High-dose eupatilin; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; COL1α1: Collagen type I alpha 1.