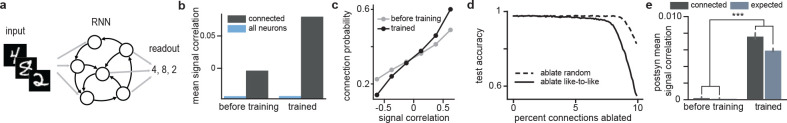
Figure 6. Like-to-like connectivity in an RNN.
a, A vanilla RNN was provided images as inputs and weights were trained so that a readout of the final state identifies the input’s label. b, Mean signal correlations among all (blue) and connected (black) neuron pairs for the same RNN before (left) and after (right) training. Neurons were classified as connected when their weights exceeded a fixed threshold. c, Connection probability as a function of signal correlation for the same network before (gray) and after (black) training. d, Test accuracy of the network as a function of the number of connections ablated when ablating random (dashed) or like-to-like (solid) connections. Connections were classified as like-to-like whenever the weight and signal correlation both exceeded a fixed threshold. e, Mean post-post signal correlations and the expected post-post signal correlation given a pairwise model similar to Fig. 5c before and after training.