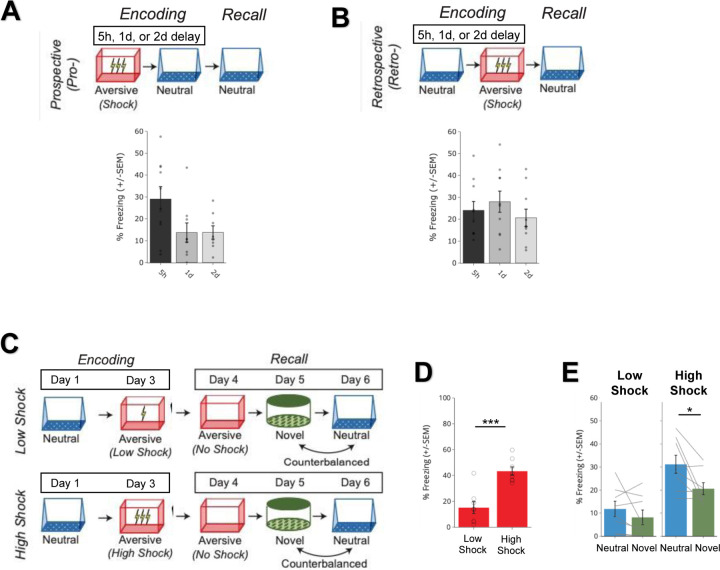
Extended Figure 1. Behavioral experiment controls.
A) Schematic to test the timecourse of prospective memory-linking (top). Mice underwent Aversive encoding and then either 5h, 1d, or 2d later they underwent Neutral encoding. The following day, mice were tested in the previously experienced Neutral context. Mice froze significantly more in the Neutral context when the Neutral context occurred within 5h of the Aversive context, compared to when it occurred one day or more after Aversive encoding (bottom). Main effect of timepoint (F2,24 = 3.689, p = 0.04) (5h, N = 10 mice; 1d, N = 9 mice; 2d, N = 8 mice). Post-hoc tests revealed a trend for higher freezing in the 5h timepoint compared to the 1d or 2d timepoints: 1d (t16.38 = 2.137, p = 0.07), 2d (t13.45 = 2.38, p = 0.07).
B) Schematic to test the timecourse of retrospective memory-linking (top). Mice underwent Neutral encoding, followed by Aversive encoding in a separate context 5h, 1d, or 2d later. The day following Aversive encoding, they were tested in the previously experienced Neutral context. Mice froze no differently in the Neutral context regardless of how long before Aversive encoding the Neutral context was experienced (bottom). No main effect of timepoint (F2,27 = 0.73, p = 0.49) (5h, N = 10 mice; 1d, N = 10 mice; 2d, N = 10 mice).
C) Schematic of low vs high shock retrospective memory-linking experiment (without calcium imaging as a replication). Mice underwent Neutral encoding followed by a low or high shock Aversive encoding two days later. In the subsequent 3 days, mice were tested in the Aversive context, and then Neutral and Novel contexts, counterbalanced.
D) Mice froze more in the Aversive context in High Shock vs Low Shock mice (t14 = 5.04, p = 0.00018) (Low Shock, N = 8 mice; High Shock, N = 8 mice).
E) High Shock mice exhibited higher freezing in Neutral vs Novel recall, while Low Shock mice did not. A priori post-hoc test: High Shock (t7 = 2.65, p = 0.033), Low Shock (t7 = 1.21, p = 0.133) (Low Shock, N = 8 mice; High Shock N = 8 mice).