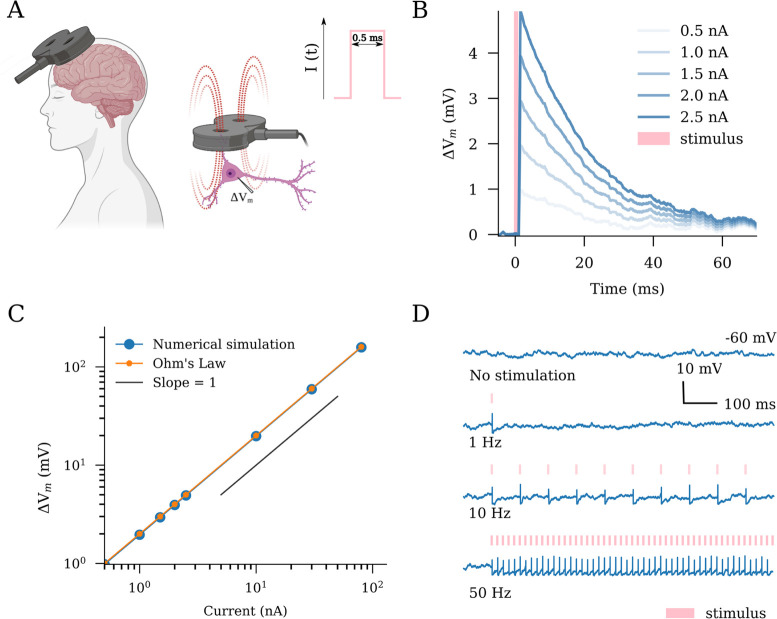
Fig 1. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has an immediate effect on the membrane potential dynamics of single neurons.
(A) Schematic illustration of TMS in humans and neurons. The TMS-induced electric fields cause depolarization of neurons in the target region. We modeled TMS as rectangular pulse current injections with a duration of 0.5 ms (c.f., standard output parameters of conventional TMS devices). (B,C) Single stimuli produce changes in the membrane potential in a dose-dependent linear manner as predicted by Ohm’s law. (D) Suprathreshold stimulation at different frequencies elicits spiking responses from the stimulated neurons. Created with BioRender.com.