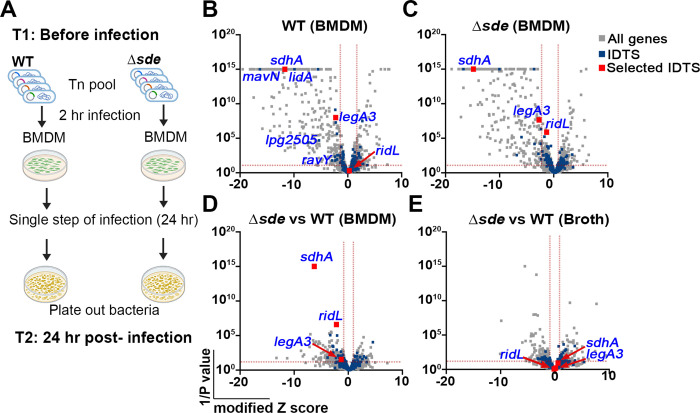
Fig. 1. Tn-seq identifies mutations that aggravate loss of Sde function.
(A) Schematic view of Tn-seq analysis to identify aggravating mutations. Himar-1 pools were constructed in parallel in SK01 (WT) and SK02 (Δsde) strains and insertion site abundance was determined after growth in broth (Materials and Methods). Three of the sequenced pools were incubated with BMDMs for 24 hrs in parallel, plated on bacteriological medium, and relative abundance of insertions was determined by HTS to determine fitness of individual mutations in the two different strain backgrounds (Materials and Methods). (B, C) Volcano plots of the relative fitness, represented as modified Z scores (Materials and Methods) comparing replication in BMDM versus AYE for either WT or Δsde strains. Candidates were identified based on criteria of ZMOD > 2 from the population median and were statistically significant (p < 0.05) based on unpaired t-test after Two-stage step-up correction (indicated by dotted red line) (73, 74). Blue font indicates IDTS that are the focus of study or which were previously shown to have an intracellular growth defect. (D) Volcano plots displaying relative fitness of insertion mutations in a Δsde background compared to the WT background for intracellular growth in BMDM. Genes were identified as candidates based > 1 MAD from the population mean and statistical significance (p < 0.05) based on unpaired t-test after Two-stage step-up correction method (74) (indicated by dotted line). Data are based on n=3 biological replicates of pools made in each strain. (E) Volcano plots of relative fitness (modified Z scores) of mutations in Δsde background versus WT background for growth in AYE broth culture. Grey, blue and red squares represent whole genes, icm/dot or Icm/Dot translocated substrate (IDTS) genes and genes selected based on the following criteria, respectively. Criteria: 1) mutations who showed fitness differences (Δsde - WT) > 1 median absolute deviation (MAD) from the population median fitness and were statistically significant based on unpaired t tests (p < 0.05; Dataset S1), 2) genes that were Icm/Dot translocated substrates, and 3) genes possibly involved in LCV biogenesis.