Fig. 3. Aggravating mutations result in loss of LCV integrity and accelerated pyroptotic cell death at early infection times.
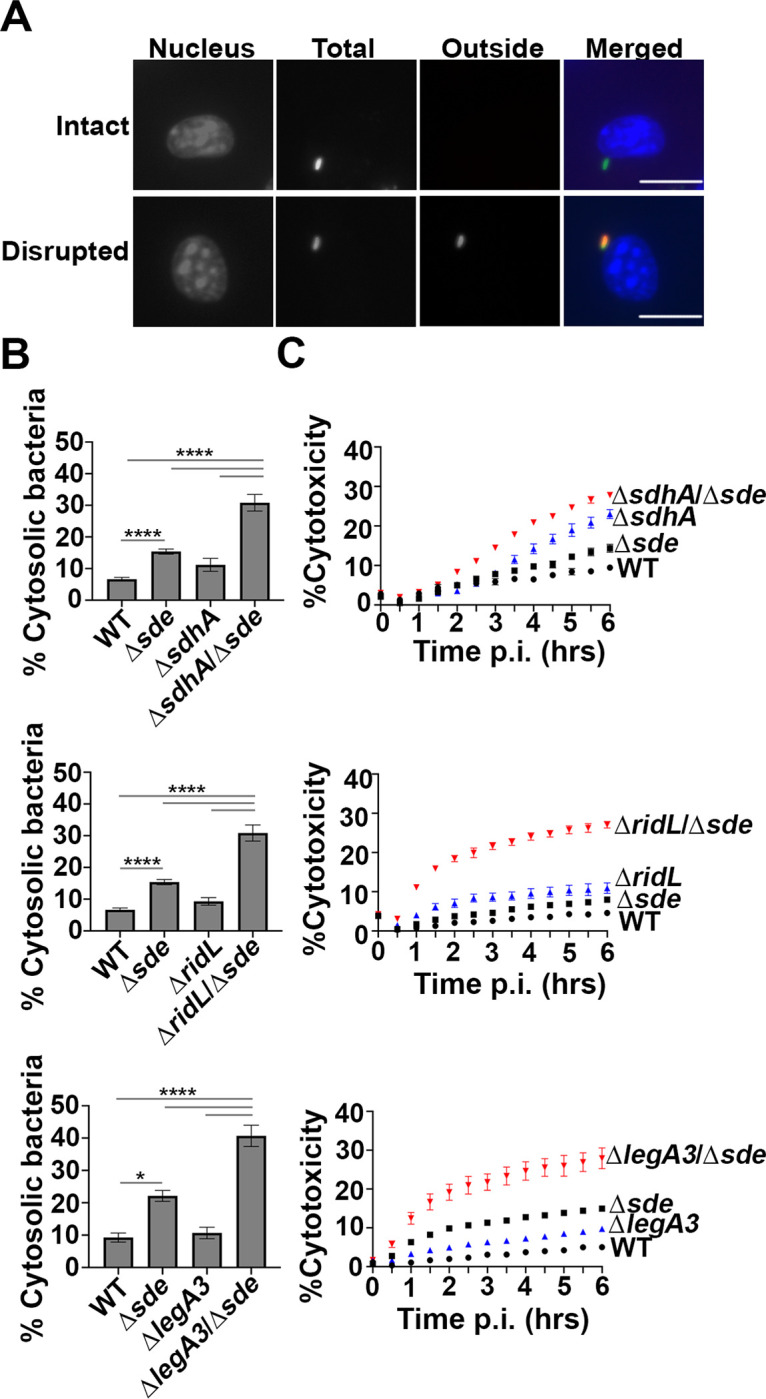
(A) Examples of cytosolic and vacuolar bacteria. Macrophages were challenged with either WT or noted mutant strains for 2 hr, fixed, probed with anti-L. pneumophila (Alexa Fluor 594 secondary, red), permeabilized, and reprobed with anti-L. pneumophila (Alexa Fluor 488 secondary, green). Cytosolic bacteria are accessible to both antibodies, shown in yellow in the merged image, whereas vacuolar bacteria are shown in green. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) Disrupted vacuole integrity of L. pneumophila strains at 2 hr post-infection. BMDMs were challenged with indicated strains, fixed and stained for bacteria before and after permeabilization. For quantification, bacteria that stained positively in the absence of permeabilization were divided by the total infected population (mean ± SEM; three biological replicates with 300 LCVs were counted per replicate) (C) Kinetics of macrophage cell death, with infection of indicated strains. BMDMs were infected with L. pneumophila WT or mutant strains and propidium iodide (PI) incorporation was used to monitor cell death. Data shown and error bars are mean ± SEM for 30 min increments and a representative of 3 biological replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons, with significance represented as: *p<0.05; ****p < 0.0001.
