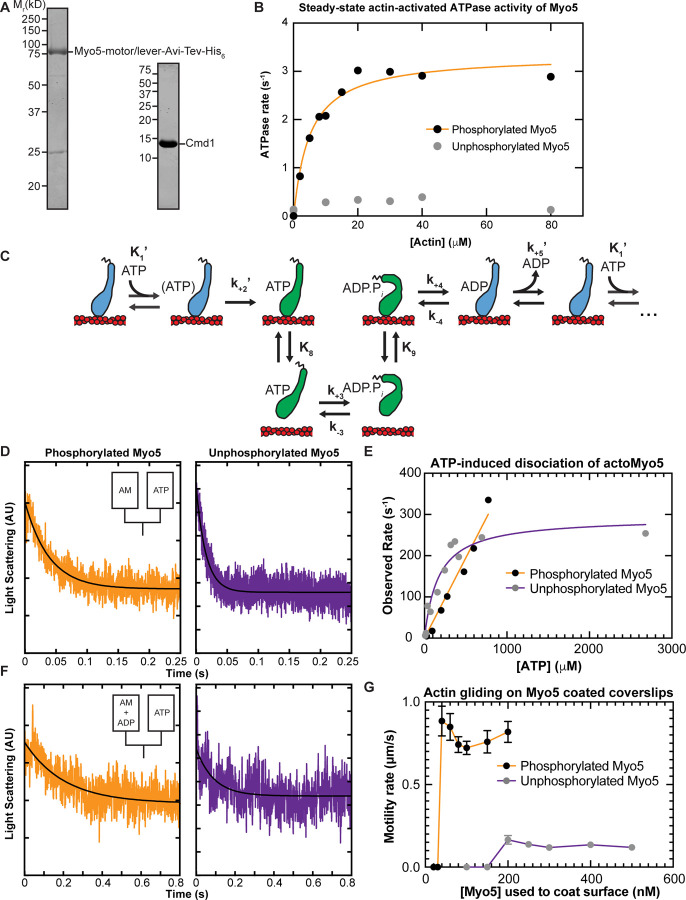
Figure 2: In-solution, population biochemical characterization of Myo5.
(A) Coomassie-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gels showing example preparations of the purified Myo5 motor/lever construct and calmodulin (Cmd1, light chain) used in all experiments. (B) The actin concentration dependence of the steady-state ATPase activity of 100 nM unphosphorylated (grey circles) and phosphorylated Myo5 (black circles). Each data point represents the average of 6–7 time courses, which were 100 s each. The orange line is a best fit of the phosphorylated Myo5 data to a rectangular hyperbola. (C) Schematic pathway for the Myo5 ATPase cycle. Blue motors are in tightly bound conformations, green motors are weakly bound/unbound. (D) Example light scattering transients reporting on ATP-induced dissociation of phosphorylated (left, ) and unphosphorylated (right, ) actoMyo5, obtained by mixing 100 nM actoMyo5 (AM) with 94 µm and 72 µM ATP, respectively, as shown in the inset schematic. The black line is the fit of a single exponential function to the data. (E) ATP concentration dependence of dissociation of 100 nM unphosphorylated (grey circles) and phosphorylated actoMyo5 (black circles). Each data point represents 3–6 time courses averaged and fit to a single exponential decay function. The orange line is a linear best fit of the phosphorylated Myo5 data. The purple line is a best fit of the unphosphorylated Myo5 data to a rectangular hyperbola. (F) Example light scattering transients reporting ATP-induced dissociation of ADP-saturated phosphorylated (left) and unphosphorylated (right) actoMyo5, obtained by preincubating 200 nM actoMyo5 (AM) with 100 µM ADP, then mixing rapidly with 2.5 mM ATP, as shown in the inset schematic. The black line is the fit of a single exponential function to the data. (G) Velocity of actin filament gliding, measured at varying surface densities of Phospho-Myo5 (black circles, orange line) and unphosphorylated Myo5 (gray circles, purple line) in in vitro motility assays. Myosin concentrations indicate the quantity of protein incubated in the flow chamber before washing. Each data point represents the average velocity of 30 – 60 filaments, and the error bars are standard deviations.