Figure 8. PonA1 rescues the morphological defects of ΔmptA.
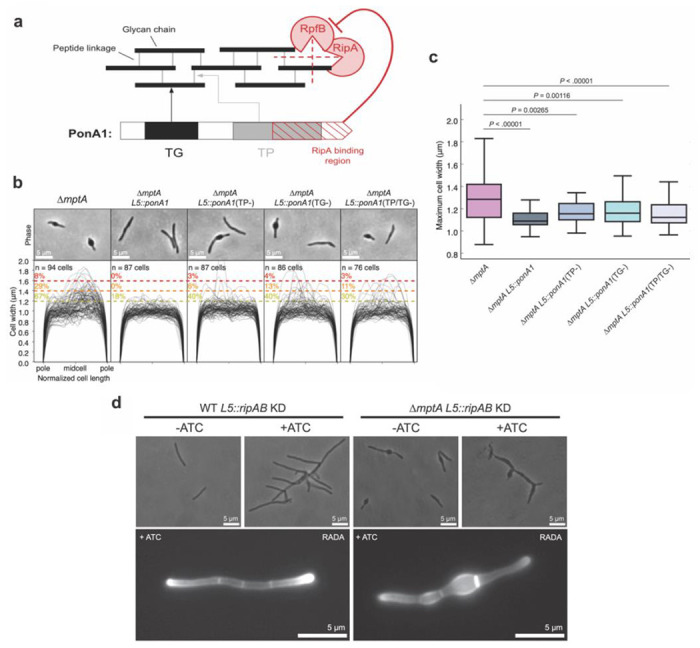
a) The domain structure of PonA1 and the corresponding cell wall substrates and interacting partners. TG, transglycosylase domain; TP, transpeptidase domain. The dotted red lines indicate which peptidoglycan structures are hydrolyzed by each component of the cell wall hydrolase complex comprised of RipA and RpfB. b) Phase micrographs and cell width profiles of ΔmptA cells overexpressing nothing (ΔmptA), fully functional PonA1 (ΔmptA + PonA1), transpeptidase-deficient PonA1 (ΔmptA + PonA1(TP−)), transglycosylase-deficient PonA1 (ΔmptA + PonA1(TG−)), and transpeptidase/transglycosylase deficient PonA1 (ΔmptA + PonA1(TP/TG−)). c) Boxplots comparing the distribution of maximum cell widths between ΔmptA and each PonA1 overexpression strain. d) (Top) Phase micrographs of ATC-inducible ripAB CRISPRi knock down strains constructed in the WT and ΔmptA genetic backgrounds. (Bottom) Fluorescent micrographs of ATC-inducible ripAB knock down strains stained with RADA.
