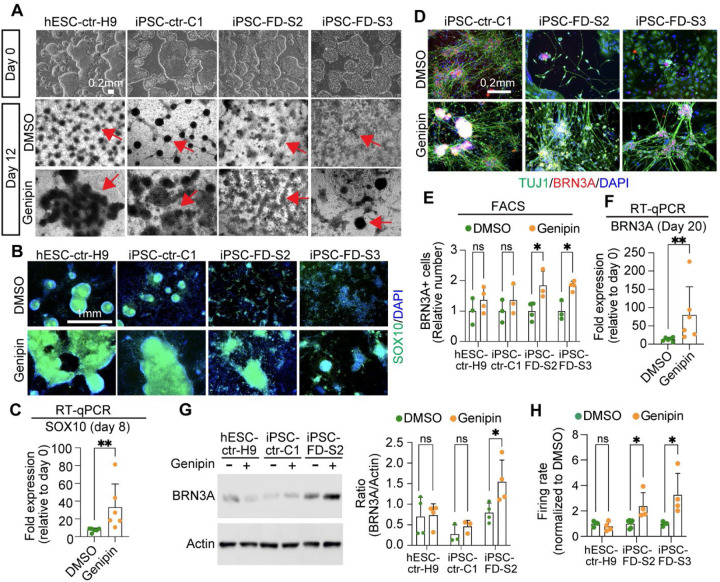
Figure 3. Genipin rescues neural crest and sensory neuron-related phenotypes in FD.
A) hPSC lines look normal at the pluripotent stage (day 0), but differentiation into NC cells is diminished in the FD lines (DMSO, dark ridges/red arrow indicate NC cells); this is rescued by genipin (10 µM) treatment. B and C) SOX10 expression is restored in NC cells upon genipin treatment. Cells were differentiated in the presence of genipin (10 µM) and fixed on day 12. B) Cells were stained for SOX10 and DAPI and analyzed by IF. n=5 biological replicates. C) Genipin increases SOX10 expression. RNA isolated from FD cells differentiated in the presence of genipin (10 µM) was analyzed by RT-qPCR. n=6 biological replicates. D-F) Genipin restores SN differentiation. iPSC-FD-S2 and iPSC-FD-S3 cells were treated with genipin (10 µM) and differentiated into SNs. RNA was isolated on day 20 or cells were fixed and stained using the indicated antibodies and analyzed by D) IF (n=5 biological replicates), E) intracellular flow cytometry (n=3–4 biological replicates), and F) RT-qPCR (n=6 biological replicates). G) Western blot analysis confirms the increase in SN production upon genipin treatment. Cells differentiated with genipin (10 µM) were lysed on day 20 and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (left) and quantified (right). n=3–4 biological replicates. H) Genipin increases firing rate of FD SNs. Cells were differentiated in the presence of genipin (10 µM) and firing rate was analyzed by MEA. n=4–6 biological replicates. In C, E, F, G, H, Two-tailed Student’s t-test. ns, non-significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.005. All graphs show mean ± s.d. Data from iPSC-FD-S2 and iPSC-FD-S3 are pooled as FD in C and F.