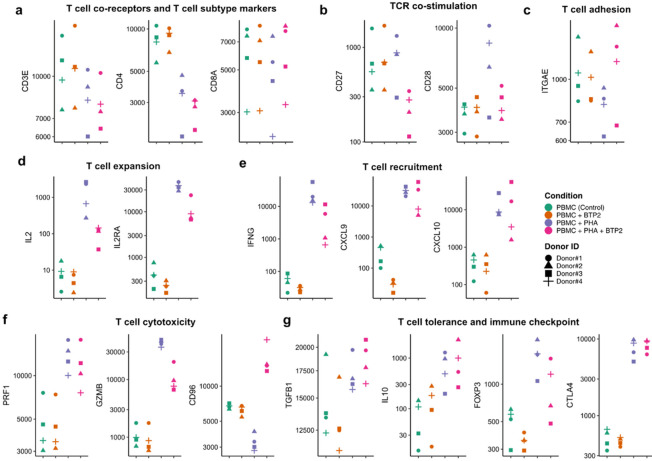
Figure 2. Differential effects of BTP2 on PHA-induced alterations in the expression of mRNAs encoding proteins involved in T cells expansion, recruitment, activation, effector function, and tolerance.
(a-g) Jitter plots showing the log-normalized counts across the four treatment conditions. (a) Pan-T cell surface antigen receptor complex CD3E, CD4 expressed on T helper cells and responsible for recognition of antigenic peptide in the context of HLA class II antigens and CD8 expressed on cytotoxic T cells and responsible for recognition of antigenic peptide in the context of HLA class I antigens; (b) T cell co-stimulation receptors CD27 and CD28; (c) T cell adhesion marker: surface integrin ITGAE (CD103); (d) T cell growth factor IL2 and its receptor IL2RA responsible for T cell clonal expansion; (e) IFNG induced T cell recruitment/homing proteins: Chemoattractant molecules CXCL9 and CXCL10; (f) T cell cytotoxic proteins PRF1 and GZMB and an antagonist of cytolytic activity, CD96. (g) Immunosuppressive cytokines TGFB1 and IL10, Treg cell marker FOXP3 and the master negative regulator of immunity CTLA4.