Figure 4. Malat1 binds to Tead3 to inhibit Nfatc1 activity and osteoclastogenesis.
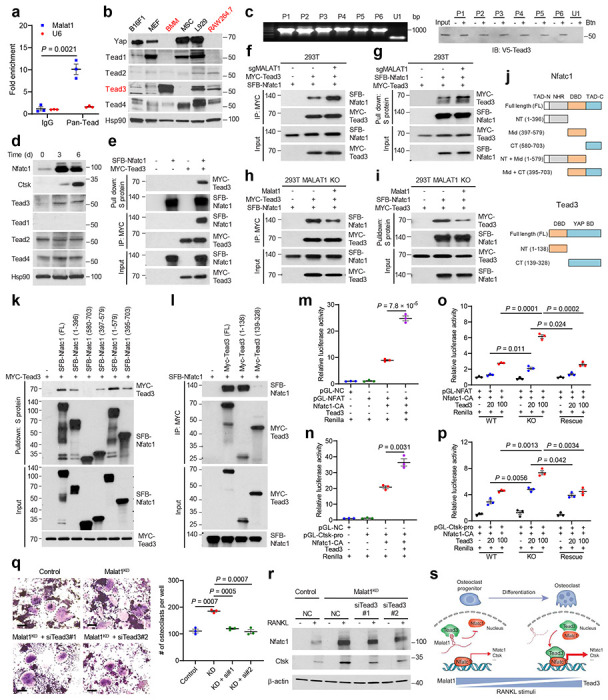
a. RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. Tead proteins were immunoprecipitated from cross-linked RAW264.7 cells by a pan-Tead-specific antibody. Tead-bound Malat1 was quantitated by qPCR. The nuclear RNA U6 was used as a negative control.
b. Immunoblotting of Yap, Tead1, Tead2, Tead3,Tead4, and Hsp90 in B16F1, MEF, BMM, MSC, L929, and RAW264.7 cells.
c. RNA pulldown assay. Unlabeled and biotinylated (Btn) Malat1 fragments (P1-P6) were synthesized by in vitro transcription (left panel), incubated with the lysate of HEK293T cells overexpressing V5-tagged Tead3, and pulled down with streptavidin beads. The bound proteins were eluted by boiling in Laemmli sample buffer and immunoblotted with a V5-specific antibody (right panel).
d. Immunoblotting of Nfatc1, Ctsk, Tead1, Tead2, Tead3, Tead4, and β-actin in RAW264.7 cells treated with RANKL (50 ng/mL) for the indicated times.
e. HEK293T cells co-transfected with SFB-Nfatc1 and MYC-Tead3 were subjected to pulldown with S-protein beads or a MYC-specific antibody, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MYC and FLAG.
f, g. Control and MALAT1-knockout HEK293T cells co-transfected with SFB-Nfatc1 and MYC-Tead3 were subjected to pulldown with a MYC-specific antibody (f) or S-protein beads (g), followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MYC and FLAG.
h, i. MALAT1-knockout and Malat1-restored HEK293T cells co-transfected with SFB-Nfatc1 and MYC-Tead3 were subjected to pulldown with a MYC-specific antibody (h) or S-protein beads (i), followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MYC and FLAG.
j. Graphical representation of mouse Nfatc1 and Tead3 proteins and their truncation mutants. The upper panel shows full-length (FL) Nfatc1 and five truncation mutants: NT (N-terminal region), Mid (middle region = DNA-binding domain, DBD), CT (C-terminal region), NT + Mid, and Mid + CT. The lower panel shows full-length Tead3 and two truncation mutants: NT (N-terminal region = DNA-binding domain) and CT (C-terminal region = YAP-binding domain).
k. HEK293T cells co-transfected with MYC-Tead3 and SFB-tagged full-length or truncated Nfatc1 were subjected to pulldown with S-protein beads, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MYC and FLAG.
l. HEK293T cells co-transfected with SFB-Nfatc1 and MYC-tagged full-length or truncated Tead3 were subjected to pulldown with a MYC-specific antibody, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against MYC and FLAG.
m, n. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with Tead3, constitutively active Nfatc1 (Nfatc1-CA), a Renilla luciferase reporter, and a firefly luciferase reporter containing tandem Nfatc1-binding sites (m) or the Ctsk promoter (n). Luciferase activity was measured 48 hours after transfection.
o, p. Wild-type, MALAT1-knockout, and Malat1-restored HEK293T cells were co-transfected with increasing amounts of Tead3, Nfatc1-CA, a Renilla luciferase reporter, and a firefly luciferase reporter containing tandem Nfatc1-binding sites (o) or the Ctsk promoter (p). Luciferase activity was measured 48 hours after transfection.
q, r. Control and Malat1-knockdown RAW264.7 cells were transfected with Tead3 siRNA or scrambled negative control (NC). 24 hours after siRNA transfection, the cells were treated with RANKL for 5 days, followed by TRAP staining and quantification (q) of multinucleated TRAP-positive cells (outlined by dashed lines). Scale bars, 100 μm. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting of Nfatc1, Ctsk, and β-actin (r).
s. Model for the regulation of osteoclastogenesis by the Malat1–Tead3–Nfatc1 axis.
Statistical significance in a and m-q was determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. Error bars are s.e.m.
