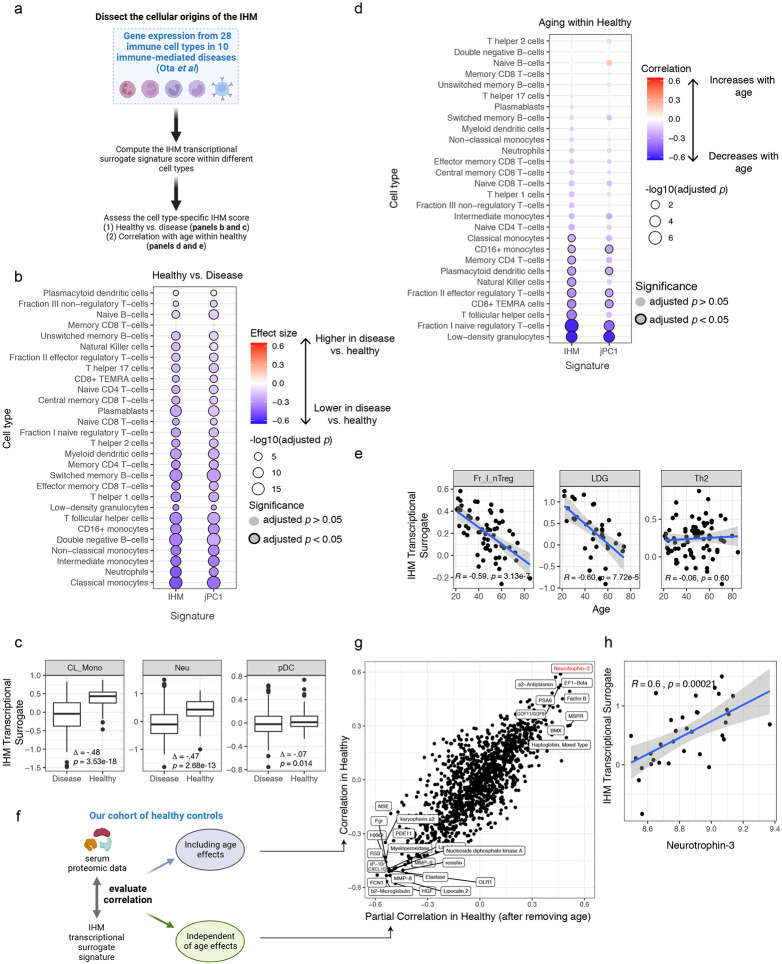
Figure 6. Cellular origin and circulating protein correlates of the IHM blood transcriptional surrogate signature.
a, Graphical overview of our analysis strategy for assessing 1) the differential expression of the IHM’s transcriptional surrogates between healthy and autoimmune disease, and 2) association with age, in each of 28 cell types from Ota et al.
b, Bubble plot showing the effect sizes and statistical significance from the comparison of autoimmune diseases vs. healthy for the IHM and jPC1 transcriptional signature scores in 28 cell types from Ota et al. Effect sizes are denoted with the color scale shown. Significance is denoted by the size of the bubble and the presence of an outline. A negative effect size represents a decrease in the signature score in individuals with autoimmune disease relative to healthy. CD8+ TEMRA = CD8+ T effector memory CD45RA+ cells.
c, Boxplots of IHM transcriptional surrogate signature scores comparing healthy controls vs. disease subjects from Ota et al. highlighting selected cell types from (b) CL_Mono: classical monocytes, Neu: neutrophil, pDC: plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Effect size (Δ) and p value are shown.
d, Bubble plot showing Pearson correlation between age and the IHM (and jPC1) transcriptional signature scores in healthy individuals only, assessed separately for each one of the 28 cell types from Ota et al. Correlation strength is denoted by the color scale shown. Significance is denoted by the size of the bubble and the presence of an outline. A negative correlation represents a decrease in the signature score with older age. A higher signature score is associated with higher immune health.
e, Scatterplots of IHM transcriptional surrogate signature scores vs. age in healthy controls from Ota et al highlighting selected cell types from (d) Fr_I_nTreg: Fraction I naive regulatory T–cells (Ota et al), LDG: low density granulocytes, Th2: T helper cells type 2. Pearson correlation and associated p value are shown.
f, Graphical overview of the analyses behind the results shown in panel (g). We aim to identify circulating proteins that are correlated with the IHM whole blood transcriptional surrogate signature in our monogenic patients and assess whether the correlation (and thus the resulting protein correlates/surrogates) depends on age (thus without or with age effects removed). The age-dependent correlation is simply the correlation between the protein levels and the IHM transcriptional surrogate, whereas the age-independent refers to the partial correlation between these values after removing the effect of age with a linear regression model.
g, Scatterplot showing the Spearman correlation values of serum proteins with the IHM transcriptional surrogate signature within healthy individuals only from the monogenic cohort. Raw Spearman correlations are shown on the y-axis, and partial correlations after removing the effect of age from the protein data and IHM transcriptional signature score are shown on the x-axis. The names of the 20 proteins with the highest absolute correlations on the x or y axes are shown. Neurotrophin-3 is highlighted in red. Correlations were computed with n = 34 healthy subjects only.
h, Scatterplot of IHM transcriptional surrogate signature score vs. Neurotrophin-3 in healthy controls from this study (n=34). Spearman correlation and associated are p value shown.