Figure 7. Transcriptome analysis of human iPSC-neurons treated with cardiac glycosides.
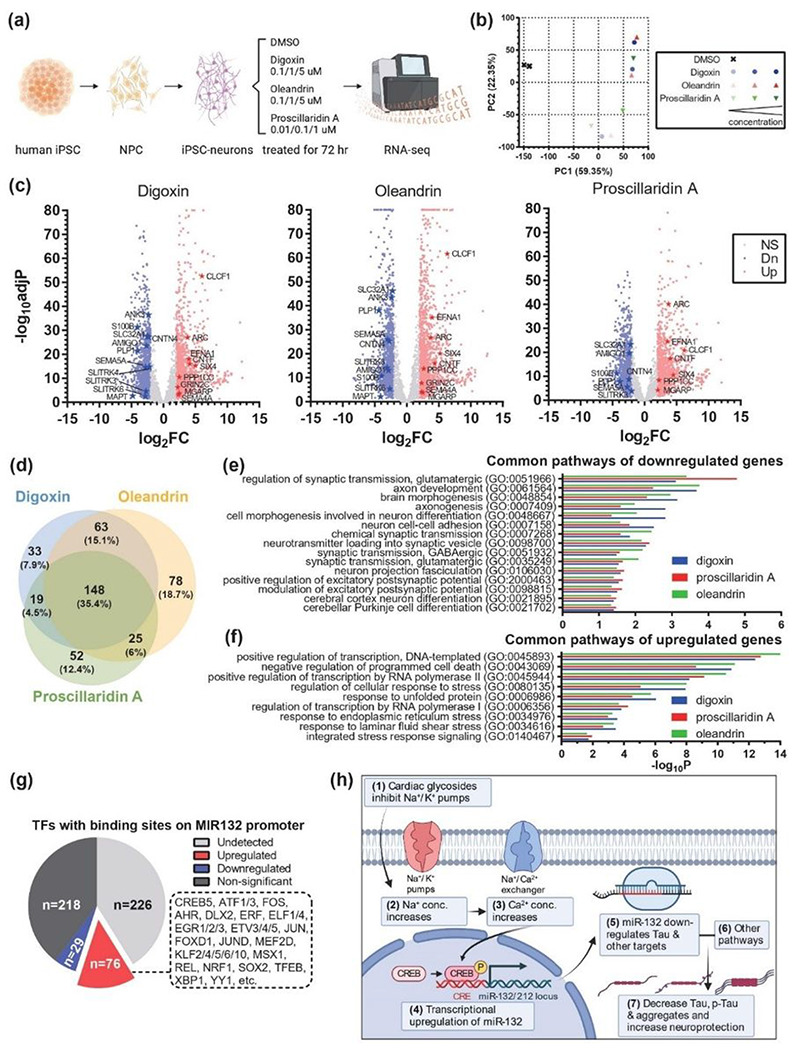
a, Workflow of the experiment design. b, Principal component analysis (PCA) indicated the strong and dose-dependent alteration of global transcriptomic profiles after treatments. c, Volcano plots showed significant down- and upregulated genes, labeled in blue and red dots, respectively. Stars highlighted dysregulated genes involved in neuronal activity and health. d, Venn diagram indicated the similarity of pathways affected by three cardiac glycosides. e, Selected neuronal pathways highlighted in common pathways of down-regulated genes. f, Selected transcription- and response-related pathways highlighted in common pathways of upregulated genes. g, Effects of cardiac glycosides on the expression of transcription factors (TFs) that have binding sites on MIR132 promoter. h, Working model showing the effects of cardiac glycosides: cardiac glycosides act through their conventional mechanism leading to the transcriptional upregulation of miR-132. The increase in miR-132, together with other pathways altered by cardiac glycosides, downregulated various forms of Tau and provided neuroprotection against toxic insults.
