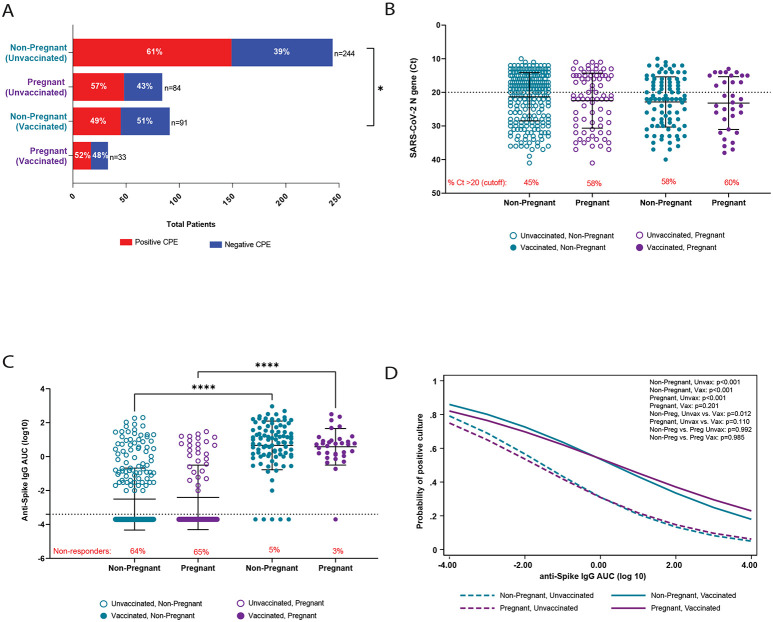
Figure 1 – SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels and antibody responses stratified by pregnancy and vaccination status.
Remnant clinical upper respiratory tract specimens were used determine rates of infectious virus recovery (A), viral RNA level (B), and anti-spike (ancestral spike) IgG titers (C) from mucosal swab samples. In (A), a positive cytopathic effect (CPE) in tissue culture was indicative of the presence of infectious virus. The dashed line in (B) represents the cutoff value (Ct ≤20) between high viral RNA and low viral levels, and the red text indicates the percentage of participants with Ct values > 20 (low viral RNA levels). The dashed line in (C) represents the limit of detection, and the red text indicates the percentage of non-responders (results below the limit of detection). Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the correlation between anti-spike IgG titer and the probability of recovery of infectious virus (D). Analysis included Fisher’s exact test (A) and) and two-way ANOVAs with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B-C). *P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. anti-S IgG, anti-ancestral strain spike immunoglobulin G; AUC, area under the curve; Ct, cycle threshold; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.