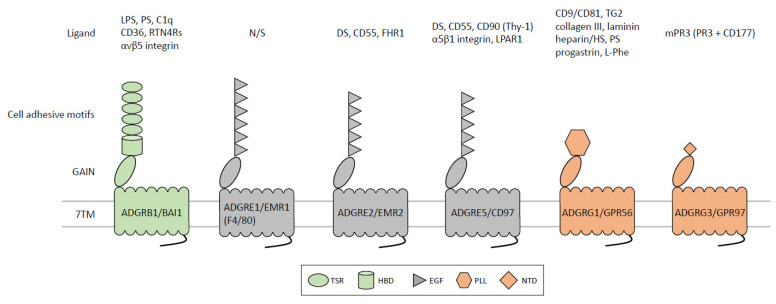
Figure 2.
Molecular and functional characteristics of immune aGPCRs. The diagram shown is selective aGPCRs involved in immune dysfunctions. Different colored shapes in the N-terminal region represent various cell-adhesive protein motifs (detailed description in the lower panel). The GAIN domain is represented by a tilted oval. Ligands/interacting partners of each immune aGPCR are shown at the top panel. Abbreviations: C1q, complement component 1q; DS, dermatan sulfate; EGF, epidermal growth factor-like; FHR1, factor H-related protein 1; HBD, hormone-binding domain; HS, heparin sulfate; LPAR1, lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NTD, N-terminal domain; PLL, pentraxin/laminin/neurexin sex-hormone-binding globulin-like; PR3, proteinase 3; PS, phosphatidylserine; RTN4Rs, Reticulon-4 receptors; TG2, transglutaminase-2; TSR, thrombospondin type 1 repeat.